Cell wounding activates phospholipase D in primary mouse keratinocytes
- PMID: 23288946
- PMCID: PMC3617934
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M027060
Cell wounding activates phospholipase D in primary mouse keratinocytes
Abstract
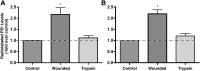
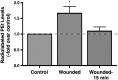
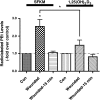
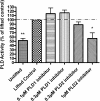
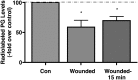
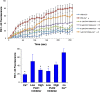
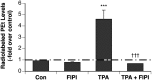
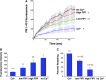
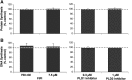
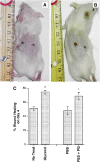
Plasma membrane disruptions occur in mechanically active tissues such as the epidermis and can lead to cell death if the damage remains unrepaired. Repair occurs through fusion of vesicle patches to the damaged membrane region. The enzyme phospholipase D (PLD) is involved in membrane traffickiing; therefore, the role of PLD in membrane repair was investigated. Generation of membrane disruptions by lifting epidermal keratinocytes from the substratum induced PLD activation, whereas removal of cells from the substratum via trypsinization had no effect. Pretreatment with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D₃, previously shown to increase PLD1 expression and activity, had no effect on, and a PLD2-selective (but not a PLD1-selective) inhibitor decreased, cell lifting-induced PLD activation, suggesting PLD2 as the isoform activated. PLD2 interacts functionally with the glycerol channel aquaporin-3 (AQP3) to produce phosphatidylglycerol (PG); however, wounding resulted in decreased PG production, suggesting a potential PG deficiency in wounded cells. Cell lifting-induced PLD activation was transient, consistent with a possible role in membrane repair, and PLD inhibitors inhibited membrane resealing upon laser injury. In an in vivo full-thickness mouse skin wound model, PG accelerated wound healing. These results suggest that PLD and the PLD2/AQP3 signaling module may be involved in membrane repair and wound healing.
Figures
References
-
- Bollag W. B., Dodd M. E., Shapiro B. A. 2004. Protein kinase D and keratinocyte proliferation. Drug News Perspect. 17: 117–126 - PubMed
-
- McNeil P. L., Kirchhausen T. 2005. An emergency response team for membrane repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6: 499–505 - PubMed
-
- McNeil P. L., Ito S. 1989. Gastrointestinal cell plasma membrane wounding and resealing in vivo. Gastroenterology. 96: 1238–1248 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

