Cardiovascular complications associated with novel angiogenesis inhibitors: emerging evidence and evolving perspectives
- PMID: 23290365
- PMCID: PMC3621011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2012.09.008
Cardiovascular complications associated with novel angiogenesis inhibitors: emerging evidence and evolving perspectives
Abstract
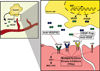
Novel cancer therapies targeting tumor angiogenesis have revolutionized treatment options in a variety of tumors. Specifically, VEGF signaling pathway (VSP) inhibitors have been introduced into clinical practice at a rapid pace over the last decade. It is becoming increasingly clear that VSP inhibitors can cause cardiovascular toxicities including hypertension, thrombosis, and heart failure. This review highlights these toxicities and proposes several strategies in their prevention and treatment. However, we recognize the dearth of data in this area and advocate a multi-disciplinary approach involving cardiologists and oncologists, as well as clinical and translational studies, in understanding and treating VSP-inhibitor associated toxicities.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe'er J, Stone J, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med. 1995;1:1024–1028. - PubMed
-
- Azizi M, Chedid A, Oudard S. Home blood-pressure monitoring in patients receiving sunitinib. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:95–97. - PubMed
-
- Baffert F, Le T, Sennino B, Thurston G, Kuo CJ, Hu-Lowe D, McDonald DM. Cellular changes in normal blood capillaries undergoing regression after inhibition of VEGF signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290:H547–H559. - PubMed
-
- Camera M, Giesen PL, Fallon J, Aufiero BM, Taubman M, Tremoli E, Nemerson Y. Cooperation between VEGF and TNF-alpha is necessary for exposure of active tissue factor on the surface of human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Chintalgattu V, Ai D, Langley RR, Zhang J, Bankson JA, Shih TL, Reddy AK, Coombes KR, Daher IN, Pati S, Patel SS, Pocius JS, Taffet GE, Buja LM, Entman ML, Khakoo AY. Cardiomyocyte PDGFR-beta signaling is an essential component of the mouse cardiac response to loadinduced stress. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:472–484. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

