Increased placental expression and maternal serum levels of apoptosis-inducing TRAIL in recurrent miscarriage
- PMID: 23290504
- PMCID: PMC3562443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2012.11.032
Increased placental expression and maternal serum levels of apoptosis-inducing TRAIL in recurrent miscarriage
Abstract
Introduction: Recurrent miscarriage (RM; ≥3 consecutive pregnancy losses) occurs in 1-3% of fertile couples. No biomarkers with high predictive value of threatening miscarriage have been identified. We aimed to profile whole-genome differential gene expression in RM placental tissue, and to determine the protein levels of identified loci in maternal sera in early pregnancy.
Methods: GeneChips (Affymetrix(®)) were used for discovery and Taqman RT-qPCR assays for replication of mRNA expression in placentas from RM cases (n = 13) compared to uncomplicated pregnancies matched for gestational age (n = 23). Concentrations of soluble TRAIL (sTRAIL) and calprotectin in maternal serum in normal first trimester (n = 35) and failed pregnancies (early miscarriage, n = 18, late miscarriage, n = 4; tubal pregnancy, n = 11) were determined using ELISA.
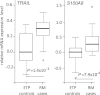
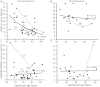
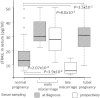
Results: In RM placentas 30 differentially expressed (with nominal P-value < 0.05) transcripts were identified. Significantly increased placental mRNA expression of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL; P = 1.4 × 10(-3); fold-change 1.68) and S100A8 (P = 7.9 × 10(-4); fold-change 2.56) encoding for inflammatory marker calprotectin (S100A8/A9) was confirmed by RT-qPCR. When compared to normal first trimester pregnancy (sTRAIL 16.1 ± 1.6 pg/ml), significantly higher maternal serum concentration of sTRAIL was detected at the RM event (33.6 ± 4.3 pg/ml, P = 0.00027), and in pregnant women, who developed an unpredicted miscarriage 2-50 days after prospective serum sampling (28.5 ± 4.4 pg/ml, P = 0.039). Women with tubal pregnancy also exhibited elevated sTRAIL (30.5 ± 3.9 pg/ml, P = 0.035). Maternal serum levels of calprotectin were neither diagnostic nor prognostic to early pregnancy failures (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: The study indicated of sTRAIL as a potential predictive biomarker in maternal serum for early pregnancy complications.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Branch D.W., Gibson M., Silver R.M. Clinical practice. Recurrent miscarriage. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1740–1747. - PubMed
-
- Berry C.W., Brambati B., Eskes T.K., Exalto N., Fox H., Geraedts J.P. The Euro-team early pregnancy (ETEP) protocol for recurrent miscarriage. Hum Reprod. 1995;10:1516–1520. - PubMed
-
- Rai R., Regan L. Recurrent miscarriage. Lancet. 2006;368:601–611. - PubMed
-
- Menasha J., Levy B., Hirschhorn K., Kardon N.B. Incidence and spectrum of chromosome abnormalities in spontaneous abortions: new insights from a 12-year study. Genet Med. 2005;7:251–263. - PubMed
-
- Philipp T., Philipp K., Reiner A., Beer F., Kalousek D.K. Embryoscopic and cytogenetic analysis of 233 missed abortions: factors involved in the pathogenesis of developmental defects of early failed pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:1724–1732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

