Widespread regulation of translation by elongation pausing in heat shock
- PMID: 23290915
- PMCID: PMC3570722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.028
Widespread regulation of translation by elongation pausing in heat shock
Abstract
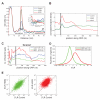
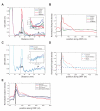
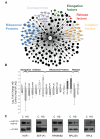
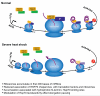
Global repression of protein synthesis is a hallmark of the cellular stress response and has been attributed primarily to inhibition of translation initiation, although this mechanism may not always explain the full extent of repression. Here, using ribosome footprinting, we show that 2 hr of severe heat stress triggers global pausing of translation elongation at around codon 65 on most mRNAs in both mouse and human cells. The genome-wide nature of the phenomenon, its location, and features of protein N termini suggested the involvement of ribosome-associated chaperones. After severe heat shock, Hsp70's interactions with the translational machinery were markedly altered and its association with ribosomes was reduced. Pretreatment with mild heat stress or overexpression of Hsp70 protected cells from heat shock-induced elongation pausing, while inhibition of Hsp70 activity triggered elongation pausing without heat stress. Our findings suggest that regulation of translation elongation in general, and by chaperones in particular, represents a major component of cellular stress responses.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abravaya K, Myers MP, Murphy SP, Morimoto RI. The human heat shock protein hsp70 interacts with HSF, the transcription factor that regulates heat shock gene expression. Genes Dev. 1992;6:1153–1164. - PubMed
-
- Ballinger DG, Pardue ML. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983;33:103–113. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann RP, Mizzen LE, Welch WJ. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990;248:850–854. - PubMed
-
- Berisio R, Schluenzen F, Harms J, Bashan A, Auerbach T, Baram D, Yonath A. Structural insight into the role of the ribosomal tunnel in cellular regulation. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:366–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

