Discovery of a novel type of autophagy targeting RNA
- PMID: 23291500
- PMCID: PMC3590259
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.23002
Discovery of a novel type of autophagy targeting RNA
Abstract
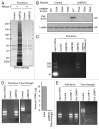
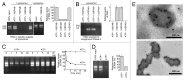
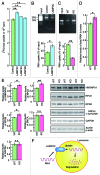
Regulated degradation of cellular components by lysosomes is essential to maintain biological homeostasis. In mammals, three forms of autophagy, macroautophagy, microautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), have been identified. Here, we showed a novel type of autophagy, in which RNA is taken up directly into lysosomes for degradation. This pathway, which we term "RNautophagy," is ATP-dependent, and unlike CMA, is independent of HSPA8/Hsc70. LAMP2C, a lysosomal membrane protein, serves as a receptor for this pathway. The cytosolic tail of LAMP2C specifically binds to almost all total RNA derived from mouse brain. The cytosolic sequence of LAMP2C and its affinity for RNA are evolutionarily conserved from nematodes to humans. Our findings shed light on the mechanisms underlying RNA homeostasis in higher eukaryotes.
Keywords: LAMP; LAMP-2; LAMP-2C; LAMP2; LAMP2C; RNA; RNautophagy; autophagy.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
