The tetraspanin CD151-ARSA mutant inhibits angiogenesis via the YRSL sequence
- PMID: 23292489
- PMCID: PMC3981038
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2012.1250
The tetraspanin CD151-ARSA mutant inhibits angiogenesis via the YRSL sequence
Erratum in
-
[Corrigendum] The tetraspanin CD151‑ARSA mutant inhibits angiogenesis via the YRSL sequence.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Oct;28(4):182. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13069. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37594051 Free PMC article.
Abstract
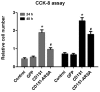
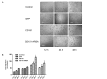
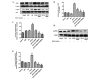
Previous studies have shown that the tetraspanin CD151 is essential for pathological or physiological angiogenesis. However, the cellular signaling mechanism and the role of the CD151 YRSL sorting motif in in vitro vasculogenesis remains unknown. In this study, the results showed that both CD151 and CD151-ARSA gene delivery were capable of increasing the expression of CD151 at the protein level in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Moreover, there was no significant difference in CD151 protein expression between the CD151 group and the CD151-ARSA group. Overexpression of CD151 promoted HUVEC cell proliferation, migration and capillary network formation in vitro. However, in the CD151-ARSA group, the abilities of cell proliferation, migration and capillary network formation were all decreased, compared with the CD151 group. Furthermore, the activation of PI3K, Akt and ERK signaling pathways was attenuated in the CD151-ARSA mutant group compared with the CD151 group. This study suggests that the YRSL motif of CD151 plays a key role in CD151-induced angiogenesis. Our observations provide insights into a new mechanism of CD151 regulating angiogenesis via vesicle trafficking.
Figures


References
-
- Fitter S, Tetaz TJ, Berndt MC, Ashman LK. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a novel platelet-endothelial cell tetra-span antigen, PETA-3. Blood. 1995;86:1348–1355. - PubMed
-
- Sincock PM, Mayrhofer G, Ashman LK. Localization of the transmembrane 4 superfamily (TM4SF) member PETA-3 (CD151) in normal human tissues: comparison with CD9, CD63, and alpha5beta1 integrin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1997;45:515–525. - PubMed
-
- Sincock PM, Fitter S, Parton RG, Berndt MC, Gamble JR, Ashman LK. PETA-3/CD151, a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, is localised to the plasma membrane and endocytic system of endothelial cells, associates with multiple integrins and modulates cell function. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:833–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

