Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP
- PMID: 23292513
- PMCID: PMC3573218
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11808
Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP
Abstract
Glucose production by the liver is essential for providing a substrate for the brain during fasting. The inability of insulin to suppress hepatic glucose output is a major aetiological factor in the hyperglycaemia of type-2 diabetes mellitus and other diseases of insulin resistance. For fifty years, one of the few classes of therapeutics effective in reducing glucose production has been the biguanides, which include phenformin and metformin, the latter the most frequently prescribed drug for type-2 diabetes. Nonetheless, the mechanism of action of biguanides remains imperfectly understood. The suggestion a decade ago that metformin reduces glucose synthesis through activation of the enzyme AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) has recently been challenged by genetic loss-of-function experiments. Here we provide a novel mechanism by which metformin antagonizes the action of glucagon, thus reducing fasting glucose levels. In mouse hepatocytes, metformin leads to the accumulation of AMP and related nucleotides, which inhibit adenylate cyclase, reduce levels of cyclic AMP and protein kinase A (PKA) activity, abrogate phosphorylation of critical protein targets of PKA, and block glucagon-dependent glucose output from hepatocytes. These data support a mechanism of action for metformin involving antagonism of glucagon, and suggest an approach for the development of antidiabetic drugs.
Figures

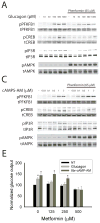

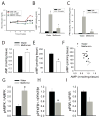
Comment in
-
Basic research: new metformin mechanism elucidated in vitro and in vivo.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013 Mar;9(3):132. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.11. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23358356 No abstract available.
References
-
- DeFronzo RA, Simonson D, Ferrannini E. Hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance: a common feature of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) and type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1982;23:313–9. - PubMed
-
- Postic C, Dentin R, Girard J. Role of the liver in the control of carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis. Diabetes Metab. 2004;30:398–408. - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:193–203. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Inzucchi SE, et al. Efficacy and metabolic effects of metformin and troglitazone in type II diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:867–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

