Therapeutic hypothermia after pediatric cardiac arrest trials: the vanguard phase experience and implications for other trials
- PMID: 23295834
- PMCID: PMC3540393
- DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e31825b860b
Therapeutic hypothermia after pediatric cardiac arrest trials: the vanguard phase experience and implications for other trials
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether an 18-month vanguard phase, in the Therapeutic Hypothermia after Pediatric Cardiac Arrest trials, confirmed study feasibility and patient safety, a prerequisite to continued funding by the sponsor.
Design: Randomized controlled trial.
Setting: Pediatric intensive care and pediatric cardiac care units in 15 clinical sites in the United States and Canada.
Patients: Children aged 48 hrs to 18 yrs of age, with return of circulation after cardiac arrest.
Interventions: Therapeutic hypothermia vs. therapeutic normothermia.
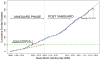
Measurements and main results: The first 15 of 20 potential sites to obtain Institutional Review Board and subcontract approvals were selected as vanguard sites. Institutional Review Board approvals were obtained 92 days (median, interquartile range 65-114) and subcontracts signed 34 days (interquartile range 20-48) after distribution. Sites screened subjects at 13 days (interquartile range 9-21) and enrolled the first subjects 64 days (interquartile range 13-154) after study launch. The recruitment milestone was reached 4 months ahead of schedule, with no safety concerns identified. Overall recruitment in this ongoing trial remains on target.
Conclusions: The Therapeutic Hypothermia after Pediatric Cardiac Arrest vanguard phase proved beneficial for the investigators and funding agency. Because complex multicenter trials are rarely ready to launch when grant funds are received, the vanguard allowed time to refine the protocol and recruitment approaches. Competition for vanguard positions led to expedient Institutional Review Board and subcontract completion. Early success and sustained momentum contributed to recruitment at or above goals. Financial risks to the sponsor were minimized by tying funding for the full trial to achieving prespecified milestones. A vanguard phase may be a desirable strategy for the successful conduct of other complex clinical trials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00878644 NCT00880087.
Figures
References
-
- Duley L, Antman K, Arena J, et al. Specific barriers to the conduct of randomized trials. Clin Trials. 2008;5:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell PH, Murphy SB, Butow PN, et al. Clinical trials in children. Lancet. 2004;364:803–811. - PubMed
-
- Field M. Ethical Conduct of Clinical Research Involving Children. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2004. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell PH, Butow PN, Craig JC. Pediatricians’ attitudes toward randomized controlled trials involving children. J Pediatr. 2002;141:798–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical