Dual role of immunomodulation by anticancer chemotherapy
- PMID: 23296003
- PMCID: PMC4045109
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3045
Dual role of immunomodulation by anticancer chemotherapy
Abstract
The anticancer efficacy of conventional chemotherapies seems to be due, in part, to augmentation of the host immune reactivity. However, a new study reveals that two common chemotherapeutic agents, gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil, can also activate immune regulatory cells, which stimulates the emergence of protumorigenic cytokines via inflammasome pathways, limiting the antitumor efficacy of the drugs (pages 57–64).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Figures
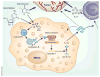
Comment on
-
Chemotherapy-triggered cathepsin B release in myeloid-derived suppressor cells activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome and promotes tumor growth.Nat Med. 2013 Jan;19(1):57-64. doi: 10.1038/nm.2999. Epub 2012 Dec 2. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23202296
References
-
- Shurin MR, Naiditch H, Gutkin DW, Umansky V, Shurin GV. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:1792–1803. - PubMed
-
- Emens LA, Jaffee EM. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8059–8064. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka F, et al. Int J Cancer. 2002;101:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Lacour S, et al. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1645–1651. - PubMed
-
- Lutsiak ME, et al. Blood. 2005;105:2862–2868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

