The burden of influenza in young children, 2004-2009
- PMID: 23296444
- PMCID: PMC3557405
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2012-1255
The burden of influenza in young children, 2004-2009
Abstract
Objective: To characterize the health care burden of influenza from 2004 through 2009, years when influenza vaccine recommendations were expanded to all children aged ≥6 months.
Methods: Population-based surveillance for laboratory-confirmed influenza was performed among children aged <5 years presenting with fever and/or acute respiratory illness to inpatient and outpatient settings during 5 influenza seasons in 3 US counties. Enrolled children had nasal/throat swabs tested for influenza by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and their medical records reviewed. Rates of influenza hospitalizations per 1000 population and proportions of outpatients (emergency department and clinic) with influenza were computed.
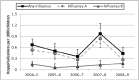
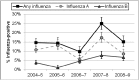
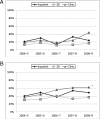
Results: The study population comprised 2970, 2698, and 2920 children from inpatient, emergency department, and clinic settings, respectively. The single-season influenza hospitalization rates were 0.4 to 1.0 per 1000 children aged <5 years and highest for infants <6 months. The proportion of outpatient children with influenza ranged from 10% to 25% annually. Among children hospitalized with influenza, 58% had physician-ordered influenza testing, 35% had discharge diagnoses of influenza, and 2% received antiviral medication. Among outpatients with influenza, 7% were tested for influenza, 7% were diagnosed with influenza, and <1% had antiviral treatment. Throughout the 5 study seasons, <45% of influenza-negative children ≥6 months were fully vaccinated against influenza.
Conclusions: Despite expanded vaccination recommendations, many children are insufficiently vaccinated, and substantial influenza burden remains. Antiviral use was low. Future studies need to evaluate trends in use of vaccine and antiviral agents and their impact on disease burden and identify strategies to prevent influenza in young infants.
Figures

References
-
- Harper SA, Fukuda K, Uyeki TM, Cox NJ, Bridges CB, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) . Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2004;53(RR-6):1–40 - PubMed
-
- Smith NM, Bresee JS, Shay DK, Uyeki TM, Cox NJ, Strikas RA, Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices . Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006;55(RR-10):1–42 - PubMed
-
- Fiore AE, Shay DK, Broder K, et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) . Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2008. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57(RR-7):1–60 - PubMed
-
- Poehling KA, Edwards KM, Weinberg GA, et al. New Vaccine Surveillance Network . The underrecognized burden of influenza in young children. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(1):31–40 - PubMed
-
- Staat MA, Griffin MR, Donauer S, et al. Vaccine effectiveness for laboratory-confirmed influenza in children 6–59 months of age, 2005–2007. Vaccine. 2011;29(48):9005–9011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

