Genomic impact of transient low-dose decitabine treatment on primary AML cells
- PMID: 23297133
- PMCID: PMC3587326
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-459313
Genomic impact of transient low-dose decitabine treatment on primary AML cells
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by dysregulated gene expression and abnormal patterns of DNA methylation; the relationship between these events is unclear. Many AML patients are now being treated with hypomethylating agents, such as decitabine (DAC), although the mechanisms by which it induces remissions remain unknown. The goal of this study was to use a novel stromal coculture assay that can expand primary AML cells to identify the immediate changes induced by DAC with a dose (100nM) that decreases total 5-methylcytosine content and reactivates imprinted genes (without causing myeloid differentiation, which would confound downstream genomic analyses). Using array-based technologies, we found that DAC treatment caused global hypomethylation in all samples (with a preference for regions with higher levels of baseline methylation), yet there was limited correlation between changes in methylation and gene expression. Moreover, the patterns of methylation and gene expression across the samples were primarily determined by the intrinsic properties of the primary cells, rather than DAC treatment. Although DAC induces hypomethylation, we could not identify canonical target genes that are altered by DAC in primary AML cells, suggesting that the mechanism of action of DAC is more complex than previously recognized.
Figures
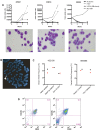
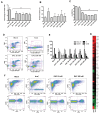


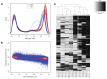

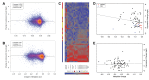
Comment in
-
Demethylation demystification.Blood. 2013 Feb 28;121(9):1488-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-483735. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23449614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowenberg B. Strategies in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2004;89(9):1029–1032. - PubMed
-
- Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116(3):354–365. - PubMed
-
- Schlenk RF, Dohner K, Krauter J, et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(18):1909–1918. - PubMed
-
- Cashen AF, Schiller GJ, O'Donnell MR, DiPersio JF. Multicenter, phase II study of decitabine for the first-line treatment of older patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(4):556–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

