Noncanonical GPCR signaling arising from a PTH receptor-arrestin-Gβγ complex
- PMID: 23297229
- PMCID: PMC3557057
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1205756110
Noncanonical GPCR signaling arising from a PTH receptor-arrestin-Gβγ complex
Abstract
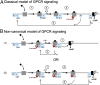
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) participate in ubiquitous transmembrane signal transduction processes by activating heterotrimeric G proteins. In the current "canonical" model of GPCR signaling, arrestins terminate receptor signaling by impairing receptor-G-protein coupling and promoting receptor internalization. However, parathyroid hormone receptor type 1 (PTHR), an essential GPCR involved in bone and mineral metabolism, does not follow this conventional desensitization paradigm. β-Arrestins prolong G protein (G(S))-mediated cAMP generation triggered by PTH, a process that correlates with the persistence of arrestin-PTHR complexes on endosomes and which is thought to be associated with prolonged physiological calcemic and phosphate responses. This presents an inescapable paradox for the current model of arrestin-mediated receptor-G-protein decoupling. Here we show that PTHR forms a ternary complex that includes arrestin and the Gβγ dimer in response to PTH stimulation, which in turn causes an accelerated rate of G(S) activation and increases the steady-state levels of activated G(S), leading to prolonged generation of cAMP. This work provides the mechanistic basis for an alternative model of GPCR signaling in which arrestins contribute to sustaining the effect of an agonist hormone on the receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Calvert PD, et al. Membrane protein diffusion sets the speed of rod phototransduction. Nature. 2001;411(6833):90–94. - PubMed
-
- Lohse MJ, Benovic JL, Codina J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Beta-arrestin: A protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 1990;248(4962):1547–1550. - PubMed
-
- Lohse MJ, et al. Receptor-specific desensitization with purified proteins. Kinase dependence and receptor specificity of beta-arrestin and arrestin in the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin systems. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(12):8558–8564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

