Comparative analysis of radon, thoron and thoron progeny concentration measurements
- PMID: 23297318
- PMCID: PMC3709658
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrs129
Comparative analysis of radon, thoron and thoron progeny concentration measurements
Abstract
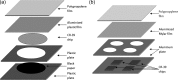
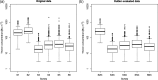
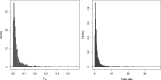
This study examined correlations between radon, thoron and thoron progeny concentrations based on surveys conducted in several different countries. For this purpose, passive detectors developed or modified by the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) were used. Radon and thoron concentrations were measured using passive discriminative radon-thoron detectors. Thoron progeny measurements were conducted using the NIRS-modified detector, originally developed by Zhuo and Iida. Weak correlations were found between radon and thoron as well as between thoron and thoron progeny. The statistical evaluation showed that attention should be paid to the thoron equilibrium factor for calculation of thoron progeny concentrations based on thoron measurements. In addition, this evaluation indicated that radon, thoron and thoron progeny were independent parameters, so it would be difficult to estimate the concentration of one from those of the others.
Keywords: radon; thoron; thoron equilibrium factor; thoron progeny.
Figures






References
-
- Žunić ZS, Kobal I, Vaupotič J, et al. High natural radiation exposure in radon spa areas: a detailed field investigation in Niška Banja (Balkan region) J Environ Radioactiv. 2006;89:249–60. - PubMed
-
- Žunić ZS, Kozak K, Ciotoli G, et al. A campaign of discrete radon concentration measurements in soil of Niška Banja town, Serbia. Radiat Meas. 2007;42:1696–702.
-
- Žunić ZS, Janik M, Tokonami S, et al. Field experience with soil gas mapping using Japanese passive radon/thoron discriminative detectors for comparing high and low radiation areas in Serbia (Balkan Region). J. Radiat Res. 2009;50:355–61. - PubMed
-
- Yamada Y, Sun Q, Tokonami S, et al. Radon-thoron discriminative measurements in Gansu province, China, and their implication for dose estimates. J Toxicol Env Heal A. 2006;69:723–34. - PubMed
-
- Tokonami S, Sun Q, Akiba S, et al. Radon and thoron exposures for cave residents in Shanxi and Shaanxi Provinces. Radiat Res. 2004;162:390–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

