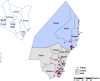
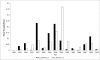
Shifts in malaria vector species composition and transmission dynamics along the Kenyan coast over the past 20 years
- PMID: 23297732
- PMCID: PMC3544599
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-13
Shifts in malaria vector species composition and transmission dynamics along the Kenyan coast over the past 20 years
Abstract
Background: Over the past 20 years, numerous studies have investigated the ecology and behaviour of malaria vectors and Plasmodium falciparum malaria transmission on the coast of Kenya. Substantial progress has been made to control vector populations and reduce high malaria prevalence and severe disease. The goal of this paper was to examine trends over the past 20 years in Anopheles species composition, density, blood-feeding behaviour, and P. falciparum sporozoite transmission along the coast of Kenya.
Methods: Using data collected from 1990 to 2010, vector density, species composition, blood-feeding patterns, and malaria transmission intensity was examined along the Kenyan coast. Mosquitoes were identified to species, based on morphological characteristics and DNA extracted from Anopheles gambiae for amplification. Using negative binomial generalized estimating equations, mosquito abundance over the period were modelled while adjusting for season. A multiple logistic regression model was used to analyse the sporozoite rates.
Results: Results show that in some areas along the Kenyan coast, Anopheles arabiensis and Anopheles merus have replaced An. gambiae sensu stricto (s.s.) and Anopheles funestus as the major mosquito species. Further, there has been a shift from human to animal feeding for both An. gambiae sensu lato (s.l.) (99% to 16%) and An. funestus (100% to 3%), and P. falciparum sporozoite rates have significantly declined over the last 20 years, with the lowest sporozoite rates being observed in 2007 (0.19%) and 2008 (0.34%). There has been, on average, a significant reduction in the abundance of An. gambiae s.l. over the years (IRR = 0.94, 95% CI 0.90-0.98), with the density standing at low levels of an average 0.006 mosquitoes/house in the year 2010.
Conclusion: Reductions in the densities of the major malaria vectors and a shift from human to animal feeding have contributed to the decreased burden of malaria along the Kenyan coast. Vector species composition remains heterogeneous but in many areas An. arabiensis has replaced An. gambiae as the major malaria vector. This has important implications for malaria epidemiology and control given that this vector predominately rests and feeds on humans outdoors. Strategies for vector control need to continue focusing on tools for protecting residents inside houses but additionally employ outdoor control tools because these are essential for further reducing the levels of malaria transmission.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous