Attenuation of cocaine and heroin seeking by μ-opioid receptor antagonism
- PMID: 23299095
- PMCID: PMC3622002
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-012-2949-9
Attenuation of cocaine and heroin seeking by μ-opioid receptor antagonism
Abstract
Rationale: Evidence has implicated the endogenous opioids, in particular μ-opioid receptors, in emotional behavior and regulation of reward circuits, especially in the context of heroin addiction and hedonic responses to ingestive rewards. The μ-opioid receptor antagonist naltrexone (NTX) has been reported to be effective in preventing relapse to alcoholism and in reducing alcohol and cocaine craving during abstinence.
Objectives: The aim of the present experiments was to investigate the effects of a novel selective μ-opioid receptor antagonist GSK1521498 on cocaine and heroin seeking and the primary reinforcement of drug self-administration behavior.
Methods: Rats were first trained to self-administer cocaine or heroin and then to seek the drugs over prolonged periods of time under a second-order schedule of reinforcement, in which responding is maintained by contingent presentation of a drug-associated conditioned reinforcer. On a stable baseline, animals were treated with either GSK1521498 (0.1, 1, 3 mg/kg; IP) or NTX (0.1, 1, 3 mg/kg; SC) before each test session.
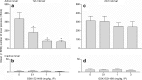
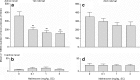
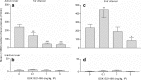
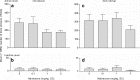
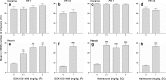
Results: Cocaine seeking was dose-dependently decreased following GSK1521498 treatment. However, the same treatment had no effect on cocaine self-administration under a continuous reinforcement schedule. Treatment with NTX had a less pronounced but similar effect. GSK1521498, but not NTX, dose-dependently reduced heroin seeking both before and after infusion of the drug although both increased heroin self-administration under continuous reinforcement.
Conclusions: These data suggest that GSK1521498, by reducing opioid receptor signaling at the μ-opioid receptor, may have therapeutic potential to reduce the propensity to seek cocaine or heroin and, additionally, to diminish the consequence of an initial relapse to heroin taking.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of opioid transmission at the μ-opioid receptor prevents both food seeking and binge-like eating.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Nov;37(12):2643-52. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.128. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22805601 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel μ-Opioid Receptor Antagonist GSK1521498 Decreases Both Alcohol Seeking and Drinking: Evidence from a New Preclinical Model of Alcohol Seeking.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Dec;40(13):2981-92. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.152. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26044906 Free PMC article.
-
The opioid receptor pharmacology of GSK1521498 compared to other ligands with differential effects on compulsive reward-related behaviours.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Jan;232(1):305-14. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3666-3. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 24973897 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Cues, Conditioned Reinforcement, and Drug Seeking: The Sequelae of a Collaborative Venture With Athina Markou.Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Jun 1;83(11):924-931. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29100631 Review.
-
Self-administration of cocaine, cannabis and heroin in the human laboratory: benefits and pitfalls.Addict Biol. 2009 Jan;14(1):9-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00121.x. Epub 2008 Oct 9. Addict Biol. 2009. PMID: 18855806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of acute oral naltrexone on the subjective and physiological effects of oral D-amphetamine and smoked cocaine in cocaine abusers.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Nov;38(12):2427-38. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.143. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23736314 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sigma-1 receptor mediates acquisition of alcohol drinking and seeking behavior in alcohol-preferring rats.Behav Brain Res. 2015;287:315-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.03.065. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25848705 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of alcohol on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the selective mu-opioid receptor antagonist GSK1521498 in healthy subjects.J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;53(10):1078-90. doi: 10.1002/jcph.110. Epub 2013 Aug 11. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23934621 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Novel approaches for the treatment of psychostimulant and opioid abuse - focus on opioid receptor-based therapies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014 Nov;9(11):1333-44. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.964203. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25253272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for a Long-Lasting Compulsive Alcohol Seeking Phenotype in Rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Mar;43(4):728-738. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.105. Epub 2017 May 29. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28553834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arroyo M, Markou A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ. Acquisition, maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration under a second-order schedule of reinforcement in rats: effects of conditioned cues and continuous access to cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1998;140:331–344. doi: 10.1007/s002130050774. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

