Drosophila heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatase Sulf1 facilitates wingless (Wg) protein degradation
- PMID: 23300081
- PMCID: PMC3576112
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.447029
Drosophila heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatase Sulf1 facilitates wingless (Wg) protein degradation
Abstract
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans regulate various physiological and developmental processes through interactions with a number of protein ligands. Heparan sulfate (HS)-ligand binding depends on the amount and patterns of sulfate groups on HS, which are controlled by various HS sulfotransferases in the Golgi apparatus as well as extracellular 6-O-endosulfatases called "Sulfs." Sulfs are a family of secreted molecules that specifically remove 6-O-sulfate groups within the highly sulfated regions on HS. Vertebrate Sulfs promote Wnt signaling, whereas the only Drosophila homologue of Sulfs, Sulf1, negatively regulates Wingless (Wg) signaling. To understand the molecular mechanism for the negative regulation of Wg signaling by Sulf1, we studied the effects of Sulf1 on HS-Wg interaction and Wg stability. Sulf1 overexpression strongly inhibited the binding of Wg to Dally, a potential target heparan sulfate proteoglycan of Sulf1. This effect of Drosophila Sulf1 on the HS-Wg interaction is similar to that of vertebrate Sulfs. Using in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo systems, we show that Sulf1 reduces extracellular Wg protein levels, at least partly by facilitating Wg degradation. In addition, expression of human Sulf1 in the Drosophila wing disc lowers the levels of extracellular Wg protein, as observed for Drosophila Sulf1. Our study demonstrates that vertebrate and Drosophila Sulfs have an intrinsically similar activity and that the function of Sulfs in the fate of Wnt/Wg ligands is context-dependent.
Figures

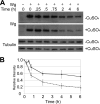

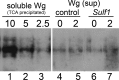

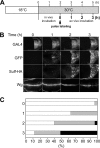


Similar articles
-
Sulfated is a negative feedback regulator of wingless in Drosophila.Dev Dyn. 2011 Mar;240(3):640-8. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22562. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Dev Dyn. 2011. PMID: 21305649 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila heparan sulfate 6-O endosulfatase regulates Wingless morphogen gradient formation.Dev Biol. 2010 Sep 15;345(2):204-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.07.006. Epub 2010 Jul 14. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20637191 Free PMC article.
-
A targeted glycan-related gene screen reveals heparan sulfate proteoglycan sulfation regulates WNT and BMP trans-synaptic signaling.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003031. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23144627 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of Drosophila glypican Dally-like in Wingless/Wnt signaling and distribution.Methods Enzymol. 2010;480:33-50. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)80002-3. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 20816203 Review.
-
Tinkering with heparan sulfate sulfation to steer development.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;17(4):173-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.02.006. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17320398 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Genetic Techniques for the Proteoglycan Functions in Drosophila.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2303:405-414. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1398-6_32. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34626396 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and characterization of Drosophila cell lines mutant for heparan sulfate modifying enzymes.Glycobiology. 2019 Jun 1;29(6):479-489. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwz020. Glycobiology. 2019. PMID: 30869121 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering functional glycosaminoglycan motifs in development.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Jun;50:144-154. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.03.011. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29579579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of HS6ST2 by miR-23b-3p enhances matrix degradation through p38 MAPK pathway in osteoarthritis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jun 13;9(6):699. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0729-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29899528 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of heparan sulfate in the niche leads to tumor-like germ cell growth in the Drosophila testis.Glycobiology. 2018 Dec 1;28(1):32-41. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwx090. Glycobiology. 2018. PMID: 29069438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esko J. D., Selleck S. B. (2002) Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 435–471 - PubMed
-
- Kirkpatrick C. A., Selleck S. B. (2007) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 120, 1829–1832 - PubMed
-
- Tabata T., Takei Y. (2004) Morphogens, their identification and regulation. Development 131, 703–712 - PubMed
-
- Kirkpatrick C. A., Knox S. M., Staatz W. D., Fox B., Lercher D. M., Selleck S. B. (2006) The function of a Drosophila glypican does not depend entirely on heparan sulfate modification. Dev. Biol. 300, 570–582 - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M., Götte M., Park P. W., Reizes O., Fitzgerald M. L., Lincecum J., Zako M. (1999) Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 729–777 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

