Interplay between calmodulin and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in Ca2+-induced inactivation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 channels
- PMID: 23300090
- PMCID: PMC3581402
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.409482
Interplay between calmodulin and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in Ca2+-induced inactivation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 channels
Abstract
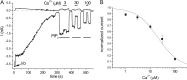
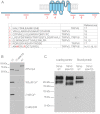
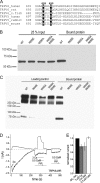
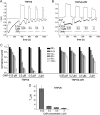
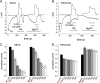
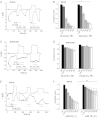
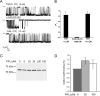
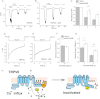
The epithelial Ca(2+) channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 (TRPV6) undergoes Ca(2+)-induced inactivation that protects the cell from toxic Ca(2+) overload and may also limit intestinal Ca(2+) transport. To dissect the roles of individual signaling pathways in this phenomenon, we studied the effects of Ca(2+), calmodulin (CaM), and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P(2)) in excised inside-out patches. The activity of TRPV6 strictly depended on the presence of PI(4,5)P(2), and Ca(2+)-CaM inhibited the channel at physiologically relevant concentrations. Ca(2+) alone also inhibited TRPV6 at high concentrations (IC(50) = ∼20 μM). A double mutation in the distal C-terminal CaM-binding site of TRPV6 (W695A/R699E) essentially eliminated inhibition by CaM in excised patches. In whole cell patch clamp experiments, this mutation reduced but did not eliminate Ca(2+)-induced inactivation. Providing excess PI(4,5)P(2) reduced the inhibition by CaM in excised patches and in planar lipid bilayers, but PI(4,5)P(2) did not inhibit binding of CaM to the C terminus of the channel. Overall, our data show a complex interplay between CaM and PI(4,5)P(2) and show that Ca(2+), CaM, and the depletion of PI(4,5)P(2) all contribute to inactivation of TRPV6.
Figures
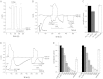
References
-
- Hoenderop J. G., Nilius B., Bindels R. J. (2005) Calcium absorption across epithelia. Physiol. Rev. 85, 373–422 - PubMed
-
- Weissgerber P., Kriebs U., Tsvilovskyy V., Olausson J., Kretz O., Stoerger C., Vennekens R., Wissenbach U., Middendorff R., Flockerzi V., Freichel M. (2011) Male fertility depends on Ca2+ absorption by TRPV6 in epididymal epithelia. Sci. Signal. 4, ra27. - PubMed
-
- Nilius B., Prenen J., Hoenderop J. G., Vennekens R., Hoefs S., Weidema A. F., Droogmans G., Bindels R. J. (2002) Fast and slow inactivation kinetics of the Ca2+ channels ECaC1 and ECaC2 (TRPV5 and TRPV6). Role of the intracellular loop located between transmembrane segments 2 and 3. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 30852–30858 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

