The circadian clock coordinates ribosome biogenesis
- PMID: 23300384
- PMCID: PMC3536797
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001455
The circadian clock coordinates ribosome biogenesis
Abstract
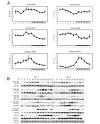
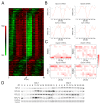
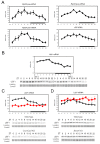
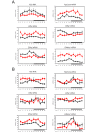
Biological rhythms play a fundamental role in the physiology and behavior of most living organisms. Rhythmic circadian expression of clock-controlled genes is orchestrated by a molecular clock that relies on interconnected negative feedback loops of transcription regulators. Here we show that the circadian clock exerts its function also through the regulation of mRNA translation. Namely, the circadian clock influences the temporal translation of a subset of mRNAs involved in ribosome biogenesis by controlling the transcription of translation initiation factors as well as the clock-dependent rhythmic activation of signaling pathways involved in their regulation. Moreover, the circadian oscillator directly regulates the transcription of ribosomal protein mRNAs and ribosomal RNAs. Thus the circadian clock exerts a major role in coordinating transcription and translation steps underlying ribosome biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Circadian genetics: Translation gets timely.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Mar;14(3):153. doi: 10.1038/nrg3429. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23338016 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhang EE, Kay SA (2010) Clocks not winding down: unravelling circadian networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11: 764–776. - PubMed
-
- Reddy AB, Karp NA, Maywood ES, Sage EA, Deery M, et al. (2006) Circadian orchestration of the hepatic proteome. Curr Biol 16: 1107–1115. - PubMed
-
- Panda S, Antoch MP, Miller BH, Su AI, Schook AB, et al. (2002) coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell 109: 307–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

