A randomized controlled trial of brain-activating rehabilitation for elderly participants with dementia in residential care homes
- PMID: 23300492
- PMCID: PMC3529563
- DOI: 10.1159/000342614
A randomized controlled trial of brain-activating rehabilitation for elderly participants with dementia in residential care homes
Abstract
Background/aims: We aimed to prove the effectiveness of brain-activating rehabilitation for dementia, which consisted of 5 principles: pleasant atmosphere, communication, praising, social role, and supportive care.
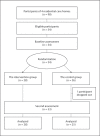
Methods: The design was a randomized controlled trial that was not blinded. Fifty-four elderly participants with dementia (mean age: 85.2 years) were selected. Intervention based on the 5 principles of brain-activating rehabilitation was conducted for 1 h, twice a week, for 12 weeks (24 sessions). The control group had no treatment. Outcome measures consisted of two observation scales, namely sum of boxes in clinical dementia rating (CDR-SB) and the multidimensional observation scale for elderly subjects (MOSES), and two cognitive tests: the Hasegawa dementia scale revised (HDS-R) and trail making test A.
Results: Repeated measure ANCOVA showed a significant interaction for total score of CDR-SB (F = 7.190, p = 0.015) and MOSES (F = 4.525, p = 0.038). There were no significant changes in the two cognitive test scores.
Conclusion: Intervention based on the principles of brain-activating rehabilitation was effective in maintaining and improving daily life functions in elderly participants with dementia in residential care homes.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Brain activity; Dementia care; Non-pharmacological therapies; Randomized clinical trials; Rehabilitation; Reminiscence therapy.
References
-
- Woods B, Spector A, Jones C, Orrell M, Davies S. Reminiscence therapy for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;CD001120 - PubMed
-
- Neal M, Briggs M. Validation therapy for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;CD001394 - PubMed
-
- Clare L, Woods RT, Moniz Cook ED, Orrell M, Spector A. Cognitive rehabilitation and cognitive training for early-stage Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;CD003260 - PubMed
-
- Haslam C, Haslam SA, Jetten J, Bevins A, Ravenscroft S, Tonks J. The social treatment: the benefits of group interventions in residential care settings. Psychol Aging. 2010;25:157–167. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi H, Maki Y, Yamagami T. Overview of non-pharmacological intervention for dementia and principles of brain-activating rehabilitation. Psychogeriatrics. 2010;10:206–213. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources