Power-laws and the use of pluripotent stem cell lines
- PMID: 23300961
- PMCID: PMC3534668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052068
Power-laws and the use of pluripotent stem cell lines
Abstract
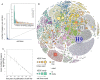
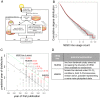
It is widely accepted that the (now reversed) Bush administration's decision to restrict federal funding for human embryonic stem cell (hESC) research to a few "eligible" hESC lines is responsible for the sustained preferential use of a small subset of hESC lines (principally the H1 and H9 lines) in basic and preclinical research. Yet, international hESC usage patterns, in both permissive and restrictive political environments, do not correlate with a specific type of stem cell policy. Here we conducted a descriptive analysis of hESC line usage and compared the ability of policy-driven processes and collaborative processes inherent to biomedical research to recapitulate global hESC usage patterns. We find that current global hESC usage can be modelled as a cumulative advantage process, independent of restrictive or permissive policy influence, suggesting a primarily innovation-driven (rather than policy-driven) mechanism underlying human pluripotent stem cell usage in preclinical research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, et al. (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282: 1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Guhr A, Kurtz A, Friedgen K, Loser P (2006) Current state of human embryonic stem cell research: an overview of cell lines and their use in experimental work. Stem Cells 24: 2187–2191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

