Discovery, validation and characterization of Erbb4 and Nrg1 haplotypes using data from three genome-wide association studies of schizophrenia
- PMID: 23301017
- PMCID: PMC3536812
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053042
Discovery, validation and characterization of Erbb4 and Nrg1 haplotypes using data from three genome-wide association studies of schizophrenia
Abstract
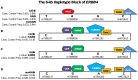
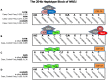
Schizophrenia is one of the most common and complex neuropsychiatric disorders, which is contributed both by genetic and environmental exposures. Recently, it is shown that NRG1-mediated ErbB4 signalling regulates many important cellular and molecular processes such as cellular growth, differentiation and death, particularly in myelin-producing cells, glia and neurons. Recent association studies have revealed genomic regions of NRG1 and ERBB4, which are significantly associated with risk of developing schizophrenia; however, inconsistencies exist in terms of validation of findings between distinct populations. In this study, we aim to validate the previously identified regions and to discover novel haplotypes of NRG1 and ERBB4 using logistic regression models and Haploview analyses in three independent datasets from GWAS conducted on European subjects, namely, CATIE, GAIN and nonGAIN. We identified a significant 6-kb block in ERBB4 between chromosome locations 212,156,823 and 212,162,848 in CATIE and GAIN datasets (p = 0.0206 and 0.0095, respectively). In NRG1, a significant 25-kb block, between 32,291,552 and 32,317,192, was associated with risk of schizophrenia in all CATIE, GAIN, and nonGAIN datasets (p = 0.0005, 0.0589, and 0.0143, respectively). Fine mapping and FastSNP analysis of genetic variation located within significantly associated regions proved the presence of binding sites for several transcription factors such as SRY, SOX5, CEPB, and ETS1. In this study, we have discovered and validated haplotypes of ERBB4 and NRG1 in three independent European populations. These findings suggest that these haplotypes play an important role in the development of schizophrenia by affecting transcription factor binding affinity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- van Os J, Kenis G, Rutten BP (2010) The environment and schizophrenia. Nature 468: 203–212. - PubMed
-
- Cardno AG, Gottesman II (2000) Twin studies of schizophrenia: from bow-and-arrow concordances to star wars Mx and functional genomics. Am J Med Genet 97: 12–17. - PubMed
-
- Falls DL (2003) Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res 284: 14–30. - PubMed
-
- Anton ES, Ghashghaei HT, Weber JL, McCann C, Fischer TM, et al. (2004) Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain. Nat Neurosci 7: 1319–1328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MH79470/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH46289/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH079469/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH079470/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046289/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- N01MH900001/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01S: MH46276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MGS U01S:MH79469/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH46318/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01S: MH67257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046318/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

