Photocatalytic degradation of bacteriophages evidenced by atomic force microscopy
- PMID: 23301095
- PMCID: PMC3536765
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053601
Photocatalytic degradation of bacteriophages evidenced by atomic force microscopy
Abstract
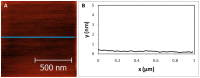
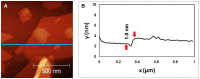
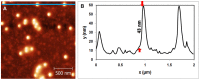
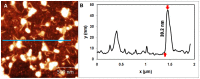
Methods to supply fresh water are becoming increasingly critical as the world population continues to grow. Small-diameter hazardous microbes such as viruses (20-100 nm diameter) can be filtered by size exclusion, but in this approach the filters are fouled. Thus, in our research, we are investigating an approach in which filters will be reusable. When exposed to ultraviolet (UV) illumination, titanate materials photocatalytically evolve (•)OH and O2(•-) radicals, which attack biological materials. In the proposed approach, titanate nanosheets are deposited on a substrate. Viruses adsorb on these nanosheets and degrade when exposed to UV light. Using atomic force microscopy (AFM), we image adsorbed viruses and demonstrate that they are removed by UV illumination in the presence of the nanosheets, but not in their absence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

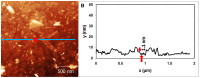
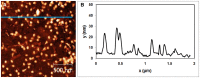
Similar articles
-
Removal of particle-associated bacteriophages by dual-media filtration at different filter cycle stages and impacts on subsequent UV disinfection.Water Res. 2007 Jun;41(11):2393-406. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.047. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Water Res. 2007. PMID: 17433406
-
Titanium dioxide mediated photocatalytic degradation of monochlorobenzene in aqueous phase.Chemosphere. 2008 Mar;71(2):398-405. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.037. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Chemosphere. 2008. PMID: 17910976
-
Photocatalytic nanolithography of self-assembled monolayers and proteins.ACS Nano. 2013 Sep 24;7(9):7610-8. doi: 10.1021/nn402063b. Epub 2013 Aug 30. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 23971891 Free PMC article.
-
An enhanced photocatalytic response of nanometric TiO2 wrapping of Au nanoparticles for eco-friendly water applications.Nanoscale. 2014 Oct 7;6(19):11189-95. doi: 10.1039/c4nr02820a. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 25125044
-
Photocatalytic degradation using design of experiments: a review and example of the Congo red degradation.J Hazard Mater. 2010 Mar 15;175(1-3):33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.050. Epub 2009 Oct 21. J Hazard Mater. 2010. PMID: 19931983 Review.
Cited by
-
An approach to the photocatalytic mechanism in the TiO2-nanomaterials microorganism interface for the control of infectious processes.Appl Catal B. 2020 Aug 5;270:118853. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118853. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Appl Catal B. 2020. PMID: 32292243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hillie T, Hlophe M (2007) Nanotechnology and the challenge of clean water. Nature Nanotechnology 2: 663–664. - PubMed
-
- Summary of the International Workshop on Nanotechnology WaDC, India, 10–12 October 2006). Meridian website. Available: http://www.merid.org/~/media/Files/Projects/nano-waterworkshop/WorkshopS.... Accessed 2012 December 4.
-
- Watts RJ, Kong S, Orr MP, Miller GC, Henry BE (1995) Photocatalytic inactivation of coliform bacteria and viruses in secondary wastewater effluent. Water Research 29: 95–100.
-
- Wong MS, Alvarez PJJ, Fang Y-l, Akcin N, Nutt MO, et al. (2008) Cleaner water using bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology 84: 158–166.
-
- Herrmann J-M, Guillard C (2000) Photocatalytic degradation of pesticides in agricultural used waters. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences 3: 417–422.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

