Focused ultrasound delivers targeted immune cells to metastatic brain tumors
- PMID: 23302230
- PMCID: PMC3607446
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2609
Focused ultrasound delivers targeted immune cells to metastatic brain tumors
Abstract
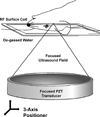
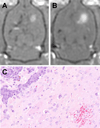
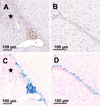
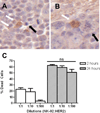
Natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic lymphocytes involved in innate immunity. NK-92, a human NK cell line, may be targeted to tumor-associated antigens in solid malignancies where it exhibits antitumor efficacy, but its clinical utility for treating brain tumors is limited by an inability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). We investigated the potential for focused ultrasound (FUS) to deliver targeted NK-92 cells to the brain using a model of metastatic breast cancer. HER2-expressing human breast tumor cells were implanted into the brain of nude rats. The NK-92-scFv(FRP5)-zeta cell line expressing a chimeric HER2 antigen receptor was transfected with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles before intravenous injection, before and following BBB disruption using focused ultrasound (551.5 kHz focused transducer, 0.33 MPa average peak rarefaction pressure) in the presence of a microbubble contrast agent. Baseline and posttreatment 1.5T and 7T MR imaging was done, and histology used to identify NK-92 cells post-mortem. Contrast-enhanced MRI showed reproducible and consistent BBB disruption. 7T MR images obtained at 16 hours posttreatment revealed a significant reduction in signal indicating the presence of iron-loaded NK-92 cells at the tumor site. The average ratio of NK-92 to tumor cells was 1:100 when NK cells were present in the vasculature at the time of sonication, versus 2:1,000 and 1:1,000 when delivered after sonication and without BBB disruption, respectively. Our results offer a preclinical proof-of-concept that FUS can improve the targeting of immune cell therapy of brain metastases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Early treatment of HER2-amplified brain tumors with targeted NK-92 cells and focused ultrasound improves survival.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Jul;18(7):974-81. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov318. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26819443 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-mediated blood-brain/blood-tumor barrier disruption improves outcomes with trastuzumab in a breast cancer brain metastasis model.J Control Release. 2012 Nov 10;163(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.09.007. Epub 2012 Sep 18. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 23000189 Free PMC article.
-
Growth inhibition in a brain metastasis model by antibody delivery using focused ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier disruption.J Control Release. 2016 Sep 28;238:281-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 3. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 27496633 Free PMC article.
-
A review of potential applications of MR-guided focused ultrasound for targeting brain tumor therapy.Neurosurg Focus. 2018 Feb;44(2):E10. doi: 10.3171/2017.11.FOCUS17620. Neurosurg Focus. 2018. PMID: 29385922 Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier disruption with low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for the treatment of pediatric brain tumors: a review and perspectives.Neurosurg Focus. 2020 Jan 1;48(1):E10. doi: 10.3171/2019.10.FOCUS19726. Neurosurg Focus. 2020. PMID: 31896084 Review.
Cited by
-
First-in-human trial of blood-brain barrier opening in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using MR-guided focused ultrasound.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 26;10(1):4373. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12426-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31558719 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Focused ultrasound-aided immunomodulation in glioblastoma multiforme: a therapeutic concept.J Ther Ultrasound. 2016 Jan 22;4:2. doi: 10.1186/s40349-016-0046-y. eCollection 2016. J Ther Ultrasound. 2016. PMID: 26807257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Clinical Trials and Approaches in the Management of Glioblastoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2024 May;26(5):439-465. doi: 10.1007/s11912-024-01519-4. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Curr Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38546941 Review.
-
Noninvasive pulsed focused ultrasound allows spatiotemporal control of targeted homing for multiple stem cell types in murine skeletal muscle and the magnitude of cell homing can be increased through repeated applications.Stem Cells. 2013 Nov;31(11):2551-60. doi: 10.1002/stem.1495. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23922277 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Positron Emission Tomography Evaluation of Topotecan Brain Kinetics after Ultrasound-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 18;13(3):405. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030405. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33803856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee Y-T. Breast carcinoma: Pattern of metastasis at autopsy. J Surg Oncol. 1983;23:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP. CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3608–3617. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Linn SC, Giaccone G, van Diest PJ, Blokhuis WM, van Der Valk P, van Kalken CK, et al. Prognostic relevance of p-glycoprotein expression in breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 1995;6:679–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

