A randomized exploratory trial of an α-7 nicotinic receptor agonist (TC-5619) for cognitive enhancement in schizophrenia
- PMID: 23303043
- PMCID: PMC3629385
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.259
A randomized exploratory trial of an α-7 nicotinic receptor agonist (TC-5619) for cognitive enhancement in schizophrenia
Abstract
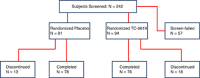
This exploratory trial was conducted to test the effects of an alpha7 nicotinic receptor partial agonist, TC-5619, on cognitive dysfunction and negative symptoms in subjects with schizophrenia. In the United States and India, 185 outpatients (18-60 years; male 69%; 46% tobacco users) with schizophrenia treated with quetiapine or risperidone monotherapy were randomized to 12 weeks of placebo (n=91) or TC-5619 (n=94; orally once daily 1 mg day 1 to week 4, 5 mg week 4 to 8, and 25 mg week 8 to 12). The primary efficacy outcome measure was the Groton Maze Learning Task (GMLT; executive function) of the CogState Schizophrenia Battery (CSB). Secondary outcome measures included: CSB composite score; Scale for Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS); Clinical Global Impression-Global Improvement (CGI-I); CGI-severity (CGI-S); and Subject Global Impression-Cognition. GMLT statistically favored TC-5619 (P=0.036) in this exploratory trial. SANS also statistically favored TC-5619 (P=0.030). No other secondary outcome measure demonstrated a drug effect in the total population; there was a statistically significant drug effect on working memory in tobacco users. The results were typically stronger in favor of TC-5619 in tobacco users and occasionally better in the United States than in India. TC-5619 was generally well tolerated with no clinically noteworthy safety findings. These results support the potential benefits of TC-5619 and alpha7 nicotinic receptor partial agonists for cognitive dysfunction and negative symptoms in schizophrenia.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association 2000Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders4th edn, Text Revision ednAmerican Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC
-
- Buchanan RW, Conley RR, Dickinson D, Ball MP, Feldman S, Gold JM, et al. Galantamine for the treatment of cognitive impairments in people with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan RW, Schwarcz R. Alpha7 nicotinic receptor agonists as cognitive treatments: is less (or less often) more. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69:5–6. - PubMed
-
- Castner SA, Smagin GN, Piser TM, Wang Y, Smith JS, Christian EP, et al. Immediate and sustained improvements in working memory after selective stimulation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69:12–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical