fosB-null mice display impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis and spontaneous epilepsy with depressive behavior
- PMID: 23303048
- PMCID: PMC3672000
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.260
fosB-null mice display impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis and spontaneous epilepsy with depressive behavior
Abstract
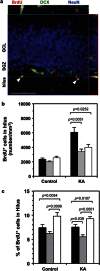
Patients with epilepsy are at high risk for major depression relative to the general population, and both disorders are associated with changes in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, although the mechanisms underlying disease onset remain unknown. The expression of fosB, an immediate early gene encoding FosB and ΔFosB/Δ2ΔFosB by alternative splicing and translation initiation, is known to be induced in neural progenitor cells within the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricles and subgranular zone of the hippocampus, following transient forebrain ischemia in the rat brain. Moreover, adenovirus-mediated expression of fosB gene products can promote neural stem cell proliferation. We recently found that fosB-null mice show increased depressive behavior, suggesting impaired neurogenesis in fosB-null mice. In the current study, we analyzed neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of fosB-null and fosB(d/d) mice that express ΔFosB/Δ2ΔFosB but not FosB, in comparison with wild-type mice, alongside neuropathology, behaviors, and gene expression profiles. fosB-null but not fosB(d/d) mice displayed impaired neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus and spontaneous epilepsy. Microarray analysis revealed that genes related to neurogenesis, depression, and epilepsy were altered in the hippocampus of fosB-null mice. Thus, we conclude that the fosB-null mouse is the first animal model to provide a genetic and molecular basis for the comorbidity between depression and epilepsy with abnormal neurogenesis, all of which are caused by loss of a single gene, fosB.
Figures

References
-
- Abbosh C, Lawkowski A, Zaben M, Gray W. GalR2/3 mediates proliferative and trophic effects of galanin on postnatal hippocampal precursors. J Neurochem. 2011;117:425–436. - PubMed
-
- Anouar Y, Lee HW, Eiden LE. Both inducible and constitutive activator protein-1-like transcription factors are used for transcriptional activation of the galanin gene by different first and second messenger pathways. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y, Cossart R. Kainate, a double agent that generates seizures: two decades of progress. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:580–587. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Canu N, Possenti R, Rinaldi AM, Trani E, Levi A. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human VGF promoter region. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1390–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

