Glucocorticoid-related molecular signaling pathways regulating hippocampal neurogenesis
- PMID: 23303060
- PMCID: PMC3672002
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.253
Glucocorticoid-related molecular signaling pathways regulating hippocampal neurogenesis
Abstract
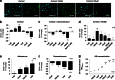
Stress and glucocorticoid hormones regulate hippocampal neurogenesis, but the molecular mechanisms underlying their effects are unknown. We, therefore, investigated the molecular signaling pathways mediating the effects of cortisol on proliferation, neuronal differentiation, and astrogliogenesis, in an immortalized human hippocampal progenitor cell line. In addition, we examined the molecular signaling pathways activated in the hippocampus of prenatally stressed rats, characterized by persistently elevated glucocorticoid levels in adulthood. In human hippocampal progenitor cells, we found that low concentrations of cortisol (100 nM) increased proliferation (+16%), decreased neurogenesis into microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2)-positive neurons (-24%) and doublecortin (Dcx)-positive neuroblasts (-21%), and increased differentiation into S100β-positive astrocytes (+23%). These effects were dependent on the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) as they were abolished by the MR antagonist, spironolactone, and mimicked by the MR-agonist, aldosterone. In contrast, high concentrations of cortisol (100 μM) decreased proliferation (-17%) and neuronal differentiation into MAP2-positive neurons (-22%) and into Dcx-positive neuroblasts (-27%), without regulating astrogliogenesis. These effects were dependent on the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), blocked by the GR antagonist RU486, and mimicked by the GR-agonist, dexamethasone. Gene expression microarray and pathway analysis showed that the low concentration of cortisol enhances Notch/Hes-signaling, the high concentration inhibits TGFβ-SMAD2/3-signaling, and both concentrations inhibit Hedgehog signaling. Mechanistically, we show that reduced Hedgehog signaling indeed critically contributes to the cortisol-induced reduction in neuronal differentiation. Accordingly, TGFβ-SMAD2/3 and Hedgehog signaling were also inhibited in the hippocampus of adult prenatally stressed rats with high glucocorticoid levels. In conclusion, our data demonstrate novel molecular signaling pathways that are regulated by glucocorticoids in vitro, in human hippocampal progenitor cells, and by stress in vivo, in the rat hippocampus.
Figures

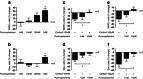
References
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 2005;437:894–897. - PubMed
-
- Anacker C, Pariante CM. Can adult neurogenesis buffer stress responses and depressive behaviour. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17:9–10. - PubMed
-
- Battista D, Ferrari CC, Gage FH, Pitossi FJ. Neurogenic niche modulation by activated microglia: transforming growth factor beta increases neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23:83–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

