Role of RACK1 in the differential proliferative effects of neuropeptide Y(1-36) and peptide YY(1-36) in SHR vs. WKY preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 23303411
- PMCID: PMC3602699
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00646.2012
Role of RACK1 in the differential proliferative effects of neuropeptide Y(1-36) and peptide YY(1-36) in SHR vs. WKY preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
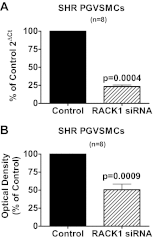
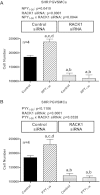
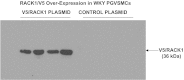
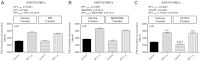
Previous studies show that neuropeptide Y(1-36) (NPY(1-36)) and peptide YY(1-36) (PYY(1-36)), by engaging Y1 receptors, stimulate proliferation of spontaneous hypertensive rat (SHR) preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells (PGVSMCs). In contrast, these peptides have little effect on proliferation of Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) PGVSMCs. Why SHR and WKY PGVSMCs differ in this regard is unknown. Because receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) can modulate cell proliferation, we tested the hypothesis that differences in RACK1 levels/localization may explain the differential response of SHR vs. WKY PGVSMCs to NPY(1-36) and PYY(1-36). Western blotting for RACK1 in subcellular fractions of cultured SHR and WKY PGVSMCs demonstrated increased levels of RACK1 in the membrane and cytoskeletal subcellular fractions of SHR vs. WKY PGVSMCs. NPY(1-36) and PYY(1-36) stimulated proliferation of SHR PGVSMCs, and siRNA knockdown of RACK1 abrogated this effect. Neither NPY(1-36) nor PYY(1-36) stimulated the proliferation of WKY PGVSMCs. However, in WKY PGVSMCs treated with a RACK1 plasmid, both NPY(1-36) and PYY(1-36) stimulated proliferation. In SHR PGVSMCs, inhibitors of the G(i)/phospholipase C/PKC pathway (a pathway known to be organized by RACK1) attenuated the ability of NPY(1-36) to stimulate the proliferation of SHR PGVSMCs. Our results suggest that RACK1 modulates the ability of PGVSMCs to respond to the proliferative actions of NPY(1-36) and PYY(1-36)and differences in RACK1 levels/localization account for, in part, differential proliferative responses to NPY(1-36) and PYY(1-36) in SHR vs. WKY PGVSMCs. Because dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors increase NPY(1-36) and PYY(1-36) levels, our findings have implications for the use of such drugs in diabetic patients.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NPY1-36 and PYY1-36 activate cardiac fibroblasts: an effect enhanced by genetic hypertension and inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase 4.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Nov;309(9):H1528-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00070.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26371160 Free PMC article.
-
RACK1 regulates angiotensin II-induced contractions of SHR preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):F565-F576. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00547.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28100502 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV regulates proliferation of preglomerular vascular smooth muscle and mesangial cells.Hypertension. 2012 Sep;60(3):757-64. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.196501. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22802229 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes, Y1 and Y2.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;611:7-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb48918.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 2174225 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y and peptide YY: major modulators of gastrointestinal blood flow and function.Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):G701-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.5.G701. Am J Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1659217 Review.
Cited by
-
ROCK/NF-κB axis-dependent augmentation of angiotensinogen by angiotensin II in primary-cultured preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Mar 15;306(6):F608-18. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00464.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24431199 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine Attenuates Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation by Inhibiting Multiple Signaling Pathways That Converge on Cyclin D.Hypertension. 2015 Dec;66(6):1207-19. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05912. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 26416848 Free PMC article.
-
NPY1-36 and PYY1-36 activate cardiac fibroblasts: an effect enhanced by genetic hypertension and inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase 4.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Nov;309(9):H1528-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00070.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26371160 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a role for the incretin system in blood pressure regulation?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Mar;16(3):417. doi: 10.1007/s11906-013-0417-5. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 24470204 Review.
-
SDF-1α (Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1α) Induces Cardiac Fibroblasts, Renal Microvascular Smooth Muscle Cells, and Glomerular Mesangial Cells to Proliferate, Cause Hypertrophy, and Produce Collagen.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Nov 7;6(11):e007253. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007253. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29114002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 270: 27489– 27494, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Ambasta RK, Ai X, Emerson CP., Jr Quail Sulf1 function requires asparagine-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem 282: 34492– 34499, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Anini Y, Fu-Cheng X, Cuber JC, Kervran A, Chariot J, Roz C. Comparison of the postprandial release of peptide YY and proglucagon-derived peptides in the rat. Pflügers Arch 438: 299– 306, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DN, Ballantyne GH, Adrian TE, Bilchik AJ, McMillen MA, Modlin IM. Adaptive increase in peptide YY and enteroglucagon after proctocolectomy and pelvic ileal reservoir construction. Dis Colon Rectum 34: 119– 125, 1991 - PubMed
-
- Barnett A. DPP-4 inhibitors and their potential role in the management of type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract 60: 1454– 1470, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

