Activation of the renin-angiotensin system by a low-salt diet does not augment intratubular angiotensinogen and angiotensin II in rats
- PMID: 23303412
- PMCID: PMC3602712
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00587.2012
Activation of the renin-angiotensin system by a low-salt diet does not augment intratubular angiotensinogen and angiotensin II in rats
Abstract
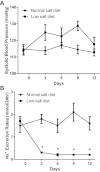
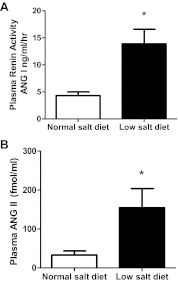
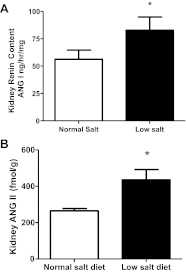
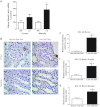
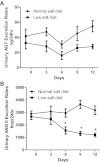
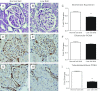
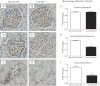
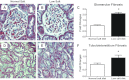
In angiotensin II (ANG II) infusion hypertension, there is an augmentation of intratubular angiotensinogen (AGT) and ANG II leading to increased urinary AGT and ANG II excretion rates associated with tissue injury. However, the changes in urinary AGT and ANG II excretion rates and markers of renal injury during physiologically induced stimulation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) by a low-salt diet remain unclear. Male Sprague-Dawley rats received a low-salt diet (0.03% NaCl; n = 6) and normal-salt diet (0.3% NaCl, n = 6) for 13 days. Low-salt diet rats had markedly higher plasma renin activity and plasma ANG II levels. Kidney cortex renin mRNA, kidney AGT mRNA, and AGT immunoreactivity were not different; however, medullary renin mRNA, kidney renin content, and kidney ANG II levels were significantly elevated by the low-salt diet. Kidney renin immunoreactivity was also markedly increased in juxtaglomerular apparati and in cortical and medullary collecting ducts. Urinary AGT excretion rates and urinary ANG II excretion rates were not augmented by the low-salt diet. The low-salt diet caused mild renal fibrosis in glomeruli and the tubulointerstitium, but no other signs of kidney injury were evident. These results indicate that, in contrast to the response in ANG II infusion hypertension, the elevated plasma and intrarenal ANG II levels caused by physiological stimulation of RAS are not reflected by increased urinary AGT or ANG II excretion rates or the development of renal injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Up-regulation of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system contributes to renal damage in high-salt induced hypertension rats].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Feb 18;47(1):149-54. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015. PMID: 25686347 Chinese.
-
Sexual dimorphism in urinary angiotensinogen excretion during chronic angiotensin II-salt hypertension.Gend Med. 2012 Aug;9(4):207-18. doi: 10.1016/j.genm.2012.06.001. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Gend Med. 2012. PMID: 22795463 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of intrarenal renin-agiotensin system contributes to renal damage in high-salt induced hypertension rats.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014;39(6):526-35. doi: 10.1159/000368463. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014. PMID: 25531334
-
Role of stimulated intrarenal angiotensinogen in hypertension.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):181-90. doi: 10.1177/1753944715585512. Epub 2015 May 18. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25987608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving concepts on regulation and function of renin in distal nephron.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Jan;465(1):121-32. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1151-6. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 22990760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Salt-Sensitive Hypertension: Perspectives on Intrarenal Mechanisms.Curr Hypertens Rev. 2015;11(1):38-48. doi: 10.2174/1573402111666150530203858. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2015. PMID: 26028244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inappropriate activity of local renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system during high salt intake: impact on the cardio-renal axis.J Bras Nefrol. 2018 Apr-Jun;40(2):170-178. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-3661. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Bras Nefrol. 2018. PMID: 29944159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary excretion of renin and angiotensinogen in hypertensive children and adolescents.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Oct 7;17(5):1325-1331. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.88482. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 34522262 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II increases fibronectin and collagen I through the β-catenin-dependent signaling in mouse collecting duct cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;308(4):F358-65. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00429.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25411386 Free PMC article.
-
The prorenin receptor in the cardiovascular system and beyond.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):H139-H145. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00373.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29101170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Hill M. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Workshop on Sodium and Blood Pressure : a critical review of current scientific evidence. Hypertension 35: 858–863, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Clavreul N, Sansilvestri-Morel P, Magard D, Verbeuren TJ, Rupin A. (Pro)renin promotes fibrosis gene expression in HEK cells through a Nox4-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300: F1310–F1318, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Du Y, Yao A, Guo D, Inagami T, Wang DH. Differential regulation of angiotensin II receptor subytpes in rat kidney by low dietary sodium. Hypertension 25: 872–877, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

