A real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of Exserohilum rostratum, a causative pathogen of fungal meningitis associated with injection of contaminated methylprednisolone
- PMID: 23303500
- PMCID: PMC3592047
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.03369-12
A real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of Exserohilum rostratum, a causative pathogen of fungal meningitis associated with injection of contaminated methylprednisolone
Abstract
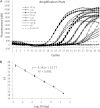
A species-specific molecular beacon real-time PCR assay was developed for rapid diagnosis of Exserohilum rostratum infection. As low as 100 fg of E. rostratum DNA can be reliably detected in the presence of 50 ng of human DNA, with a dynamic linear quantification range from 20 ng to 200 fg.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2012. Multistate outbreak of fungal infection associated with injection of methylprednisolone acetate solution from a single compounding pharmacy—United States, 2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 61:839–842 - PubMed
-
- Kauffman CA, Pappas PG, Patterson TF. 2012. Fungal infections associated with contaminated methylprednisolone injections—preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213978 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Levitz SM. 2012. Compounding drugs contaminated with fungi: a recipe for disaster. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 1:e41 doi:10.1038/emi.2012.46 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wilson LE, Blythe D, Sharfstein JM. 2012. Fungal meningitis from injection of contaminated steroids: a compounding problem. JAMA 308:2461–2462 - PubMed
-
- Brunings AM, Datnoff LE, Palmateer AJ, Locke JC, Krause CR. 2009. Exserohilum leaf spot on tiger grass. Plant Health Prog. doi:10.1094/PHP-2009-1215-01-RS. http://www.ars.usda.gov/SP2UserFiles/Place/36071000/GPRG/2009Publication... - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials