Loss of R2D2 proteins ROPN1 and ROPN1L causes defects in murine sperm motility, phosphorylation, and fibrous sheath integrity
- PMID: 23303679
- PMCID: PMC4434999
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.105262
Loss of R2D2 proteins ROPN1 and ROPN1L causes defects in murine sperm motility, phosphorylation, and fibrous sheath integrity
Abstract
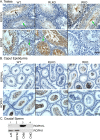
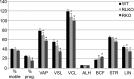
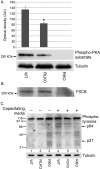
The fibrous sheath (FS) is a flagellar cytoskeletal structure unique to sperm that surrounds the outer dense fibers and axoneme. Its primary components are A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) 3 and 4, which suggests that the FS affects flagellar beating via the scaffolding of signaling pathways necessary for motility. Sperm proteins ROPN1 and ROPN1L bind AKAP3. To determine the role of ROPN1 and ROPN1L in sperm function, we created mice deficient in ROPN1 (RKO), mice deficient in ROPN1L (RLKO), and double knockout mice (DKO). All three strains of mice had normal testicular morphology and spermatogenesis. Only the DKOs had obvious defects in sperm morphology (thinning and shredding of the principal piece), which was accompanied by a reduction in AKAP3 levels. RLKO mice had slightly reduced sperm motility and increased levels of ROPN1. RKO mice had moderately impaired motility and increased levels of ROPN1L. DKO sperm were immotile. We have previously determined that RKO male mice are subfertile, and DKO males are infertile. Together these data indicate that ROPN1L and ROPN1 compensate for each other in the absence of the opposing protein, possibly to maintain AKAP3 incorporation in the FS. Sperm from mice lacking ROPN1L exhibited reductions in both cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylation of a 270-kDa protein (perhaps FSCB), and in capacitation-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Sperm from mice lacking ROPN1 had reduced levels of FSCB and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of noncapacitated sperm. These data demonstrate that mutations in ROPN1 and ROPN1L can cause defects in FS integrity, sperm motility, and PKA-dependent signaling processes, leading to male infertility.
Figures

References
-
- Remenyi A, Good MC, Lim WA. Docking interactions in protein kinase and phosphatase networks. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2006; 16: 676 685. - PubMed
-
- Carr DW, Stofko-Hahn RE, Fraser ID, Bishop SM, Acott TS, Brennan RG, Scott JD. Interaction of the regulatory subunit (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with RII-anchoring proteins occurs through an amphipathic helix binding motif. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 14188 14192. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya RP, Remenyi A, Yeh BJ, Lim WA. Domains, motifs, and scaffolds: the role of modular interactions in the evolution and wiring of cell signaling circuits. Annu Rev Biochem 2006; 75: 655 680. - PubMed
-
- Carr DW, Fujita A, Stentz CL, Liberty GA, Olson GE, Narumiya S. Identification of sperm-specific proteins that interact with A-kinase anchoring proteins in a manner similar to the type II regulatory subunit of PKA. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 17332 17338. - PubMed
-
- Eddy EM, Toshimori K, O'Brien DA. Fibrous sheath of mammalian spermatozoa. Microsc Res Tech 2003; 61: 103 115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

