Frequency of and risk factors for poor cognitive performance in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 23303848
- PMCID: PMC3590049
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31827f0f7f
Frequency of and risk factors for poor cognitive performance in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Objective: There are few detailed data on cognition in patients undergoing dialysis. We evaluated the frequency of and risk factors for poor cognitive performance using detailed neurocognitive testing.
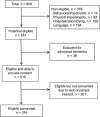
Methods: In this cross-sectional cohort study, 314 hemodialysis patients from 6 Boston-area hemodialysis units underwent detailed cognitive assessment. The neuropsychological battery assessed a broad range of functions, with established age-, sex-, and education-matched normative scores. Principal component analysis was used to derive composite scores for memory and executive function domains. Risk factors for each domain were evaluated using linear regression adjusting for age, sex, race, and education status. Analyses were repeated in those with Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score ≥ 24.
Results: Compared with population norms, patients on dialysis had significantly poorer executive function but not memory performance, a finding that persisted in the subgroup with MMSE score ≥ 24. In adjusted analyses, vascular risk factors and vascular disease were associated with lower executive function (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: There is a high frequency of poor cognitive performance in hemodialysis patients, primarily affecting executive function. Risk factors for worse executive function include vascular risk factors as well as vascular disease. Normal performance on the MMSE does not preclude impaired cognitive function, because individuals with MMSE score ≥ 24 also have a high frequency of poor cognitive performance.
References
-
- Fazekas G, Fazekas F, Schmidt R, Kapeller P, Offenbacher H, Krejs GJ. Brain MRI findings and cognitive impairment in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis treatment. J Neurol Sci 1995;134:83–88 - PubMed
-
- Kutlay S, Nergizoglu G, Duman N, et al. Recognition of neurocognitive dysfunction in chronic hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail 2001;23:781–787 - PubMed
-
- Sehgal AR, Grey SF, DeOreo PB, Whitehouse PJ. Prevalence, recognition, and implications of mental impairment among hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 1997;30:41–49 - PubMed
-
- Cannata AP, Alberoni M, Franceschi M, Mariani C. Frontal impairment in subcortical ischemic vascular dementia in comparison to Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2002;13:101–111 - PubMed
-
- Looi JC, Sachdev PS. Differentiation of vascular dementia from AD on neuropsychological tests. Neurology 1999;53:670–678 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical