Proteins and small molecules for cellular regenerative medicine
- PMID: 23303911
- PMCID: PMC3781772
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00005.2012
Proteins and small molecules for cellular regenerative medicine
Abstract
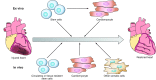
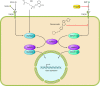
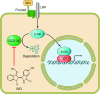
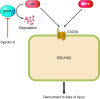
Regenerative medicine seeks to understand tissue development and homeostasis and build on that knowledge to enhance regeneration of injured tissues. By replenishing lost functional tissues and cells, regenerative medicine could change the treatment paradigm for a broad range of degenerative and ischemic diseases. Multipotent cells hold promise as potential building blocks for regenerating lost tissues, but successful tissue regeneration will depend on comprehensive control of multipotent cells-differentiation into a target cell type, delivery to a desired tissue, and integration into a durable functional structure. At each step of this process, proteins and small molecules provide essential signals and, in some cases, may themselves act as effective therapies. Identifying these signals is thus a fundamental goal of regenerative medicine. In this review we discuss current progress using proteins and small molecules to regulate tissue regeneration, both in combination with cellular therapies and as monotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Adams GB, Martin RP, Alley IR, Chabner KT, Cohen KS, Calvi LM, Kronenberg HM, Scadden DT. Therapeutic targeting of a stem cell niche. Nat Biotechnol 25: 238–243, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284: 770–776, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Askari AT, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, Goldman CK, Forudi F, Kiedrowski M, Rovner A, Ellis SG, Thomas JD, DiCorleto PE, Topol EJ, Penn MS. Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet 362: 697–703, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

