The pivotal role of TBK1 in inflammatory responses mediated by macrophages
- PMID: 23304064
- PMCID: PMC3523167
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/979105
The pivotal role of TBK1 in inflammatory responses mediated by macrophages
Abstract
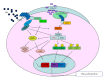
Inflammation is a complex biological response of tissues to harmful stimuli such as pathogens, cell damage, or irritants. Inflammation is considered to be a major cause of most chronic diseases, especially in more than 100 types of inflammatory diseases which include Alzheimer's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, Crohn's disease, colitis, dermatitis, hepatitis, and Parkinson's disease. Recently, an increasing number of studies have focused on inflammatory diseases. TBK1 is a serine/threonine-protein kinase which regulates antiviral defense, host-virus interaction, and immunity. It is ubiquitously expressed in mouse stomach, colon, thymus, and liver. Interestingly, high levels of active TBK1 have also been found to be associated with inflammatory diseases, indicating that TBK1 is closely related to inflammatory responses. Even though relatively few studies have addressed the functional roles of TBK1 relating to inflammation, this paper discusses some recent findings that support the critical role of TBK1 in inflammatory diseases and underlie the necessity of trials to develop useful remedies or therapeutics that target TBK1 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Moret FM, Badot V, Lauwerys BR, van Roon JA. Intraarticular soluble interleukin-17 receptor levels are increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and correlate with local mediators of inflammation: comment on the article by Pickens et al. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2012;64(2):594–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

