Mechanism of earthquake simulation as a prenatal stressor retarding rat offspring development and chinese medicine correcting the retardation: hormones and gene-expression alteration
- PMID: 23304210
- PMCID: PMC3523342
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/670362
Mechanism of earthquake simulation as a prenatal stressor retarding rat offspring development and chinese medicine correcting the retardation: hormones and gene-expression alteration
Abstract
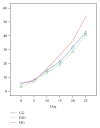
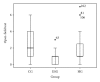
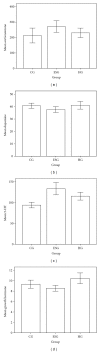
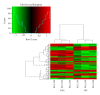
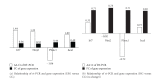
We aimed to investigate the mechanism of shaking as a prenatal stressor impacting the development of the offspring and Chinese medicines correcting the alterations. Pregnant rats were randomized into earthquake simulation group (ESG), herbal group (HG) which received herbal supplements in feed after shaking, and control group (CG). Findings revealed body weight and open field test (OFT) score of ESG offspring were statistically inferior to the CG and HG offspring. The corticosterone levels of ESG were higher than those of CG but not than HG. The dopamine level of ESG was slightly lower than that of the CG and of HG was higher than that of ESG. The 5-HT of ESG was higher than CG and HG. The growth hormone level of the ESG was significantly lower than ESG but not than CG. Gene expression profile showed 81 genes upregulated and 39 genes downregulated in ESG versus CG, and 60 genes upregulated and 28 genes downregulated in ESG versus HG. Eighty-four genes were found differentially expressed in ESG versus CG comparison and were normalized in ESG versus HG. We conclude that maternal shaking negatively affected physical and nervous system development, with specific alterations in neurohormones and gene expression. Chinese herbal medicine reduced these negative outcomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genes underlying positive influence of prenatal environmental enrichment and negative influence of prenatal earthquake simulation and corrective influence of Chinese herbal medicine on rat offspring: Irf7 and Ninj2.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 28;11(2):367-76. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i2.24. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25435624 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanism of maternal post-traumatic stress disorder in delayed rat offspring development: dysregulation of methylation and gene expression.Genet Mol Res. 2016 Aug 19;15(3). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15039009. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27706597
-
[Effects of Chinese herbal compound on monoamine and neuronal amino acids in rat's telencephalon in the course of exhaustion and recovery process].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Nov;27(4):439-43. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22295520 Chinese.
-
Intragastric Balloon Versus Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty for the Treatment of Obesity: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obes Surg. 2020 Aug;30(8):3010-3029. doi: 10.1007/s11695-020-04644-8. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 32399847 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium transport in strongly calcifying laying birds: mechanisms and regulation.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2009 Apr;152(4):447-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.11.020. Epub 2008 Dec 6. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19118637 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurobehavioral alternations of the female offspring born to polycystic ovary syndrome model rats administered by Chinese herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2021 Oct 2;16(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00512-4. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34600579 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional interventions to counteract the detrimental consequences of early-life stress.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jul;30(7):3269-3300. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03020-1. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40289212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genes underlying positive influence of prenatal environmental enrichment and negative influence of prenatal earthquake simulation and corrective influence of Chinese herbal medicine on rat offspring: Irf7 and Ninj2.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 28;11(2):367-76. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i2.24. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25435624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simpson J, Kelly JP. The impact of environmental enrichment in laboratory rats-Behavioural and neurochemical aspects. Behavioural Brain Research. 2011;222(1):246–264. - PubMed
-
- O’Donnell K, O’Connor TG, Glover V. Prenatal stress and neurodevelopment of the child: focus on the HPA axis and role of the placenta. Developmental Neuroscience. 2009;31(4):285–292. - PubMed
-
- Morley-Fletcher S, Rea M, Maccari S, Laviola G. Environmental enrichment during adolescence reverses the effects of prenatal stress on play behaviour and HPA axis reactivity in rats. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;18(12):3367–3374. - PubMed
-
- Mulder EJH, Robles De Medina PG, Huizink AC, Van Den Bergh BRH, Buitelaar JK, Visser GHA. Prenatal maternal stress: effects on pregnancy and the (unborn) child. Early Human Development. 2002;70(1-2):3–14. - PubMed
-
- Maccari S, Darnaudery M, Morley-Fletcher S, Zuena AR, Cinque C, Van Reeth O. Prenatal stress and long-term consequences: implications of glucocorticoid hormones. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2003;27(1-2):119–127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

