Myocarditis Associated with Influenza A H1N1pdm2009
- PMID: 23304476
- PMCID: PMC3533457
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/351979
Myocarditis Associated with Influenza A H1N1pdm2009
Abstract
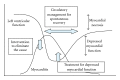
Acute myocarditis is a well-known complication of influenza infection. The frequency of myocardial involvement in influenza infection varies widely, with the clinical severity ranging from asymptomatic to fulminant varieties. The worst cases can result in death due to impaired cardiac function, although such fulminant myocarditis associated with influenza infection is rare, as shown by previous papers. Following the 2009 influenza pandemic, we reported on the clinical features of a cohort of 15 patients in Japan with H1N1pdm2009 myocarditis. In our subsequent survey of the literature for case reports or series of patients with myocarditis associated with H1N1pdm2009, we identified 58 detailed cases. We discuss here the high prevalence of fulminant myocarditis (36/58, 62%) among patients reported to have myocarditis associated with H1N1pdm2009. Mechanical circulatory support was required in 17 of the patients with fulminant myocarditis, 13 of whom recovered. We stress the need for increased awareness of influenza-associated myocarditis; such knowledge will facilitate earlier diagnosis and treatment of this fatal complication during future influenza pandemics.
Figures
References
-
- Rezkalla SH, Kloner RA. Influenza-related viral myocarditis. Wisconsin Medical Journal. 2010;109(4):209–213. - PubMed
-
- Kumar K, Guirgis M, Zieroth S, et al. Influenza myocarditis and myositis: case presentation and review of the literature. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 2011;27(4):514–522. - PubMed
-
- Mamas MA, Fraser D, Neyses L. Cardiovascular manifestations associated with influenza virus infection. International Journal of Cardiology. 2008;130(3):304–309. - PubMed
-
- Oseasohn R, Adelson L, Kaji M. Clinicopathologic study of thirty-three fatal cases of Asian influenza. The New England journal of medicine. 1959;260(11):509–518. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources