Anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects of TAK-593, a potent and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 23305239
- PMCID: PMC7657107
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12101
Anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects of TAK-593, a potent and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
Abstract
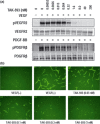
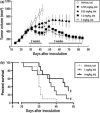
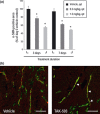
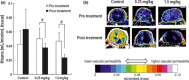
We recently reported that TAK-593, a novel imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine derivative, is a highly potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor tyrosine kinase families. Moreover, TAK-593 exhibits a uniquely long-acting inhibitory profile towards VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) and PDGF receptor β (PDGFRβ). In this study, we demonstrated that TAK-593 potently inhibits VEGF- and PDGF-stimulated cellular phosphorylation and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. TAK-593 also potently inhibits VEGF-induced tube formation of endothelial cells co-cultured with fibroblasts. Oral administration of TAK-593 exhibited strong anti-tumor effects against various human cancer xenografts along with good tolerability despite a low level of plasma exposure. Even after the blood and tissue concentrations of TAK-593 decreased below the detectable limit, a pharmacodynamic marker (phospho VEGFR2) was almost completely suppressed, indicating that its long duration of enzyme inhibition might contribute to the potent activity of TAK-593. Immunohistochemical staining indicated that TAK-593 showed anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on tumors along with a decrease of vessel density and inhibition of pericyte recruitment to microvessels in vivo. Furthermore, dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging revealed that TAK-593 reduced tumor vessel permeability prior to the onset of anti-tumor activity. In conclusion, TAK-593 is an extremely potent VEGFR/PDGFR kinase inhibitor whose potent anti-angiogenic activity suggests therapeutic potential for the treatment of solid tumors.
© 2013 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel pyrrolo[3, 2-d]pyrimidine derivative, as a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, shows potent antitumor activity by suppression of tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2012 May;103(5):939-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02238.x. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22320850 Free PMC article.
-
SKLB610: a novel potential inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(5):565-74. doi: 10.1159/000329978. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21691074
-
Biochemical characterization of TAK-593, a novel VEGFR/PDGFR inhibitor with a two-step slow binding mechanism.Biochemistry. 2011 Feb 8;50(5):738-51. doi: 10.1021/bi101777f. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21182308
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2018;59(2):455-467. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2018. PMID: 30173249 Review.
-
Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.Oncologist. 2015 Jun;20(6):660-73. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0465. Epub 2015 May 22. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26001391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The pyrazolyl-urea GeGe3 inhibits tumor angiogenesis and reveals dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK)1 as a novel angiogenesis target.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 21;8(64):108195-108212. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22598. eCollection 2017 Dec 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29296234 Free PMC article.
-
Towards discovery of novel scaffold with potent antiangiogenic activity; design, synthesis of pyridazine based compounds, impact of hinge interaction, and accessibility of their bioactive conformation on VEGFR-2 activities.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):1573-1589. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1651723. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31852269 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-126 affects ovarian cancer cell differentiation and invasion by modulating expression of vascular endothelial growth factor.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):5803-5808. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8025. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552211 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miRNA-497 inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR2.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 8;5:13827. doi: 10.1038/srep13827. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26345385 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and clinical roles of stromal PDGF receptors in tumor biology.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Dec;43(4):1593-1609. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10194-7. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38980580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 1990; 82: 4–6. - PubMed
-
- Klagsbrun M, Moses MA. Molecular angiogenesis. Chem Biol 1999; 6: R217–24. - PubMed
-
- Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia‐initiated angiogenesis. Nature 1992; 359: 843–5. - PubMed
-
- Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G et al Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science 1989; 246: 1309–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

