Miniaturized antibodies for imaging membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase in cancers
- PMID: 23305265
- PMCID: PMC7657219
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12102
Miniaturized antibodies for imaging membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase in cancers
Abstract
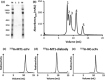
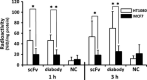
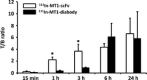
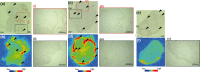
Since membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) plays pivotal roles in tumor progression and metastasis and holds great promise as an early biomarker for malignant tumors, a method of evaluating MT1-MMP expression levels would be valuable for molecular biological and clinical studies. Although we have previously developed a (99m) Tc-labeled anti-MT1-MMP monoclonal IgG ((99m) Tc-MT1-mAb) as an MT1-MMP imaging probe by nuclear medical techniques for this purpose, slow pharmacokinetics were a problem due to its large molecular size. Thus, in this study, our aim was to develop miniaturized antibodies, a single chain antibody fragment (MT1-scFv) and a dimer of two molecules of scFv (MT1-diabody), as the basic structures of MT1-MMP imaging probes followed by in vitro and in vivo evaluation with an (111) In radiolabel. Phage display screening successfully provided MT1-scFv and MT1-diabody, which had sufficiently high affinity for MT1-MMP (KD = 29.8 and 17.1 nM). Both (111) In labeled miniaturized antibodies showed higher uptake in MT1-MMP expressing HT1080 cells than in non-expressing MCF7 cells. An in vivo biodistribution study showed rapid pharmacokinetics for both probes, which exhibited >20-fold higher tumor to blood radioactivity ratios (T/B ratio), an index for in vivo imaging, than (99m) Tc-MT1-mAb 6 h post-administration, and significantly higher tumor accumulation in HT1080 than MCF7 cells. SPECT images showed heterogeneous distribution and ex vivo autoradiographic analysis revealed that the radioactivity distribution profiles in tumors corresponded to MT1-MMP-positive areas. These findings suggest that the newly developed miniaturized antibodies are promising probes for detection of MT1-MMP in cancer cells.
© 2013 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radioiodinated Peptidic Imaging Probes for in Vivo Detection of Membrane Type-1 Matrix Metalloproteinase in Cancers.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(9):1375-82. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00314. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 26328493
-
Development of a radiolabeled probe for detecting membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase on malignant tumors.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Jul;32(7):1272-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.1272. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19571397
-
Development of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase-specific activatable fluorescent probe for malignant tumor detection.Cancer Sci. 2011 Oct;102(10):1897-903. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02020.x. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21718387
-
Imaging with radiolabelled anti-membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) antibody: potentials for characterizing atherosclerotic plaques.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010 Nov;37(11):2093-104. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1521-2. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20625725
-
Radioimmunodetection of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase relevant to tumor malignancy with a pre-targeting method.Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(9):1589-95. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1589. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. PMID: 20823579
Cited by
-
The role of preclinical SPECT in oncological and neurological research in combination with either CT or MRI.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014 May;41 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S36-49. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2685-3. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24895751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of a MMP-2 activity-dependent anchoring probe for nuclear imaging of cancer.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e102180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102180. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010662 Free PMC article.
-
Gallium-68-labeled anti-HER2 single-chain Fv fragment: development and in vivo monitoring of HER2 expression.Mol Imaging Biol. 2015 Feb;17(1):102-10. doi: 10.1007/s11307-014-0769-5. Mol Imaging Biol. 2015. PMID: 25049073
-
Imaging methods to evaluate tumor microenvironment factors affecting nanoparticle drug delivery and antitumor response.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021;4(2):382-413. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.94. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34796317 Free PMC article.
-
Development of anti-membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase nanobodies as immunoPET probes for triple negative breast cancer imaging.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 24;9:1058455. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1058455. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36507540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J, Condeelis J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2005; 17: 559–64. - PubMed
-
- Jones JL, Glynn P, Walker RA. Expression of MMP‐2 and MMP‐9, their inhibitors, and the activator MT1‐MMP in primary breast carcinomas. J Pathol 1999; 189: 161–8. - PubMed
-
- Ohuchi E, Imai K, Fujii Y, Sato H, Seiki M, Okada Y. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase digests interstitial collagens and other extracellular matrix macromolecules. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 2446–51. - PubMed
-
- Knäuper V, Will H, López‐Otin C et al Cellular mechanisms for human procollagenase‐3 (MMP‐13) activation. Evidence that MT1‐MMP (MMP‐14) and gelatinase a (MMP‐2) are able to generate active enzyme. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 17124–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

