Functional significance of erythropoietin in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23305401
- PMCID: PMC3554558
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-14
Functional significance of erythropoietin in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
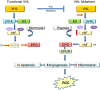
One of the molecules regulated by the transcription factor, hypoxia inducible factor (HIF), is the hypoxia-responsive hematopoietic factor, erythropoietin (EPO). This may have relevance to the development of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), where mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene are major risk factors for the development of familial and sporadic RCC. VHL mutations up-regulate and stabilize HIF, which in turn activates many downstream molecules, including EPO, that are known to promote angiogenesis, drug resistance, proliferation and progression of solid tumours. HIFs typically respond to hypoxic cellular environment. While the hypoxic microenvironment plays a critical role in the development and progression of tumours in general, it is of special significance in the case of RCC because of the link between VHL, HIF and EPO. EPO and its receptor, EPOR, are expressed in many cancers, including RCC. This limits the use of recombinant human EPO (rhEPO) to treat anaemia in cancer patients, because the rhEPO may be stimulatory to the cancer. EPO may also stimulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in RCC, and pathological EMT has a key role in cancer progression. In this mini review, we summarize the current knowledge of the role of EPO in RCC. The available data, either for or against the use of EPO in RCC patients, are equivocal and insufficient to draw a definitive conclusion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship of erythropoietin overexpression with von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor gene mutations between hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and -2α in sporadic clear cell renal carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2010 Dec;26(6):907-12. doi: 10.3892/ijmm_00000541. Int J Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 21042786
-
The erythropoietin/erythropoietin receptor signaling pathway promotes growth and invasion abilities in human renal carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045122. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028796 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Erythropoietin Activity in Clear Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3777. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083777. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332447 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Associated with Von Hippel-Lindau Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 22;18(11):2495. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112495. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29165391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The VHL/HIF oxygen-sensing pathway and its relevance to kidney disease.Kidney Int. 2006 Apr;69(8):1302-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000221. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16531988 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Genes Involved in Porphyrin Biosynthesis Pathway in the Human Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Fluoresc. 2015 Sep;25(5):1363-9. doi: 10.1007/s10895-015-1626-x. Epub 2015 Aug 6. J Fluoresc. 2015. PMID: 26245452
-
Erythropoietin is a JAK2 and ERK1/2 effector that can promote renal tumor cell proliferation under hypoxic conditions.J Hematol Oncol. 2013 Sep 3;6:65. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-65. J Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24004818 Free PMC article.
-
Cephalomannine inhibits hypoxia-induced cellular function via the suppression of APEX1/HIF-1α interaction in lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 14;12(5):490. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03771-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33990544 Free PMC article.
-
HIF2 Inactivation and Tumor Suppression with a Tumor-Directed RNA-Silencing Drug in Mice and Humans.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 15;28(24):5405-5418. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0963. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36190432 Free PMC article.
-
Human rhabdomyosarcoma cells express functional erythropoietin receptor: Potential therapeutic implications.Int J Oncol. 2015 Nov;47(5):1989-97. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3184. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26412593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eble J, Sauter G, Epstein J, Sesterhenn I. Pathology and genetics. Tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARC Press; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

