The Children's Attention Project: a community-based longitudinal study of children with ADHD and non-ADHD controls
- PMID: 23305499
- PMCID: PMC3547722
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-18
The Children's Attention Project: a community-based longitudinal study of children with ADHD and non-ADHD controls
Abstract
Background: Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects approximately 5% of children worldwide and results in significant impairments in daily functioning. Few community-ascertained samples of children with ADHD have been studied prospectively to identify factors associated with differential outcomes. The Children's Attention Project is the first such study in Australia, examining the mental health, social, academic and quality of life outcomes for children with diagnostically-confirmed ADHD compared to non-ADHD controls. The study aims to map the course of ADHD symptoms over time and to identify risk and protective factors associated with differential outcomes.
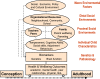
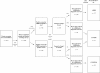
Methods/design: The sample for this prospective longitudinal study is being recruited across 43 socio-economically diverse primary schools across Melbourne, Australia. All children in Grade 1, the second year of formal schooling (6-8 years), are screened for ADHD symptoms using independent parent and teacher reports on the Conners' 3 ADHD index (~N = 5260). Children screening positive for ADHD by both parent and teacher report, and a matched sample (gender, school) screening negative, are invited to participate in the longitudinal study. At baseline this involves parent completion of the NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children IV (DISC-IV) to confirm likely ADHD diagnostic status and identify other mental health difficulties, direct child assessments (cognitive, academic, language and executive functioning; height and weight) and questionnaires for parents and teachers assessing outcomes, as well as a broad range of risk and protective factors (child, parent/family, teacher/school, and socio-economic factors). Families will be initially followed up for 3 years.
Discussion: This study is the first Australian longitudinal study of children with ADHD and one of the first community-based longitudinal studies of diagnostically confirmed children with ADHD. The study's examination of a broad range of risk and protective factors and ADHD-related outcomes has the potential to inform novel strategies for intervention and prevention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A longitudinal study of risk and protective factors associated with successful transition to secondary school in youth with ADHD: prospective cohort study protocol.BMC Pediatr. 2016 Jan 28;16:20. doi: 10.1186/s12887-016-0555-4. BMC Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26822230 Free PMC article.
-
ADHD and emotional engagement with school in the primary years: Investigating the role of student-teacher relationships.Br J Educ Psychol. 2020 Jun;90 Suppl 1:193-209. doi: 10.1111/bjep.12316. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Br J Educ Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31654412
-
A process for developing community consensus regarding the diagnosis and management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Pediatrics. 2005 Jan;115(1):e97-104. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-0953. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15629972
-
Do parents and children agree on rating a child's HRQOL? A systematic review and Meta-analysis of comparisons between children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and children with typical development using the PedsQLTM.Disabil Rehabil. 2019 Feb;41(3):265-275. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2017.1391338. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Disabil Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 29057670
-
Is ADHD a way of conceptualizing long-term emotional stress and social disadvantage?Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 3;10:966900. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.966900. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36424967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations Between Limbic System White Matter Structure and Socio-Emotional Functioning in Children with ADHD + ASD.J Autism Dev Disord. 2021 Aug;51(8):2663-2672. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04738-3. J Autism Dev Disord. 2021. PMID: 33043414
-
Analysis of personal and family factors in the persistence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: results of a prospective follow-up study in childhood.PLoS One. 2015 May 29;10(5):e0128325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128325. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26024216 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in MRI head motion across development: typical development and ADHD.Brain Imaging Behav. 2024 Oct;18(5):1144-1152. doi: 10.1007/s11682-024-00910-w. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Brain Imaging Behav. 2024. PMID: 39190098 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic age across development in children and adolescents with ADHD.Psychiatry Res. 2025 Mar;345:116373. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2025.116373. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Psychiatry Res. 2025. PMID: 39855016
-
Improving survey response rates from parents in school-based research using a multi-level approach.PLoS One. 2015 May 11;10(5):e0126950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126950. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25961851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hiscock H, Roberts G, Efron D, Sewell JR, Bryson HE, Price AM, Oberklaid F, South M, Wake MA. Children attending paediatricians study: a national prospective audit of outpatient practice from the Australian Paediatric Research Network. Med J Aust. 2011;194:392–397. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text revision) Washington, DC: Author; 2000.
-
- Barkley RA. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. 3. New York: Guilford; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical