Aberrant T-cell antigen expression in classical Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with decreased event-free survival and overall survival
- PMID: 23305738
- PMCID: PMC3591799
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-439455
Aberrant T-cell antigen expression in classical Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with decreased event-free survival and overall survival
Abstract
Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) rarely express T-cell-associated antigens (TCA), but the clinical significance of this finding is uncertain. Fifty cHLs expressing any TCA on the HRS cells (TCA-cHL) were identified in two cohorts (National Cancer Institute, n = 38; Basel, n = 12). Diagnostic pathology data were examined in all cases with additional T-cell receptor γ rearrangements (TRG@) polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in a subset of cases. The outcome data were compared with a cohort of cHLs negative for TCA (n = 272). Primary end points examined were event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS). The median age in the TCA-cHL group was 40 years (range, 10-85 years). Seventy percent presented in low stage (stage I/II) at presentation with nodular sclerosis (NS) histology predominating in 80% of cases. Among the TCA, CD4 and CD2 were most commonly expressed, seen in 80.4% and 77.4% of cases, respectively. TRG@ PCR was negative for clonal rearrangements in 29 of 31 cases. During a median follow up of 113 months, TCA expression predicted shorter OS (adjusted hazard ratio [HRadj] = 3.32 [95% confidence interval (CI): 1.61, 6.84]; P = .001) and EFS (HRadj = 2.55 [95% CI: 1.45, 4.49]; P = .001). TCA-cHL often display NS histology, lack T-cell genotype, and are independently associated with significantly shorter OS and EFS compared with TCA-negative cHLs.
Figures



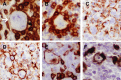

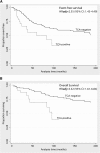
Similar articles
-
Rare expression of T-cell markers in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma.Mod Pathol. 2005 Dec;18(12):1542-9. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800473. Mod Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16056244
-
Gene rearrangement and comparative genomic hybridization studies of classic Hodgkin lymphoma expressing T-cell antigens.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006 Dec;130(12):1772-9. doi: 10.5858/2006-130-1772-GRACGH. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006. PMID: 17149949
-
Gene expression profiling of microdissected Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells correlates with treatment outcome in classical Hodgkin lymphoma.Blood. 2012 Oct 25;120(17):3530-40. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-439570. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22955918 Clinical Trial.
-
Apoptosis of Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma revisited.APMIS. 2010 May;118(5):339-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2010.02600.x. APMIS. 2010. PMID: 20477808 Review.
-
Evidence of abortive plasma cell differentiation in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma.Hematol Oncol. 2005 Sep-Dec;23(3-4):127-32. doi: 10.1002/hon.764. Hematol Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16342298 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathobiology of hodgkin lymphoma.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2014 Jun 5;6(1):e2014040. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2014.040. eCollection 2014. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24959337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma: biomarkers, drugs, and clinical trials for translational science and medicine.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 11;7(41):67551-67573. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11509. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27563824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Primary Pulmonary Hodgkin Lymphoma (PPHL): Two Institutional Experiences with Comprehensive Literature Review of 115 PPHL Cases.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 23;12(1):126. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010126. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36614926 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangement analysis of classic Hodgkin lymphoma using a BIOMED-2 assay: a paraffin-embedded tissue analysis of one hundred cases.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2024;64(2):138-143. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.24027. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2024. PMID: 38925974 Free PMC article.
-
Primary pulmonary Hodgkin's lymphoma mimicking rheumatoid arthritis-associated organizing pneumonia: A case report.Thorac Cancer. 2021 May;12(10):1620-1624. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13952. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33811475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hasenclever D, Diehl V. A prognostic score for advanced Hodgkin’s disease. International Prognostic Factors Project on Advanced Hodgkin’s Disease. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(21):1506–1514. - PubMed
-
- Tzankov A, Matter MS, Dirnhofer S. Refined prognostic role of CD68-positive tumor macrophages in the context of the cellular micromilieu of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Pathobiology. 2010;77(6):301–308. - PubMed
-
- Farinha P, Rodrigues S, Fernandes T, et al. Lymphoma Associated Macrophages Predict Survival in Uniformly Treated Patients with Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. San Antonio, TX: United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology; 2011.
-
- Chetaille B, Bertucci F, Finetti P, et al. Molecular profiling of classical Hodgkin lymphoma tissues uncovers variations in the tumor microenvironment and correlations with EBV infection and outcome. Blood. 2009;113(12):2765–3775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

