Anatomical and functional characterization of a duodeno-pancreatic neural reflex that can induce acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 23306082
- PMCID: PMC3602681
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00012.2012
Anatomical and functional characterization of a duodeno-pancreatic neural reflex that can induce acute pancreatitis
Abstract
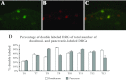
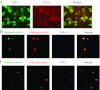
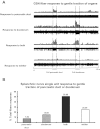
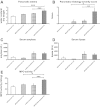
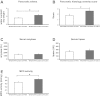
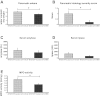
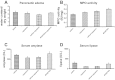
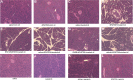
Neural cross talk between visceral organs may play a role in mediating inflammation and pain remote from the site of the insult. We hypothesized such a cross talk exists between the duodenum and pancreas, and further it induces pancreatitis in response to intraduodenal toxins. A dichotomous spinal innervation serving both the duodenum and pancreas was examined, and splanchnic nerve responses to mechanical stimulation of these organs were detected. This pathway was then excited on the duodenal side by exposure to ethanol followed by luminal mustard oil to activate transient receptor potential subfamily A, member 1 (TRPA1). Ninety minutes later, pancreatic inflammation was examined. Ablation of duodenal afferents by resiniferatoxin (RTX) or blocking TRPA1 by Chembridge (CHEM)-5861528 was used to further investigate the duodeno-pancreatic neural reflex via TRPA1. ~40% of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) from the spinal cord originated from both duodenum and pancreas via dichotomous peripheral branches; ~50% splanchnic nerve single units responded to mechanical stimulation of both organs. Ethanol sensitized TRPA1 currents in cultured DRG neurons. Pancreatic edema and myeloperoxidase activity significantly increased after intraduodenal ethanol followed by mustard oil (but not capsaicin) but significantly decreased after ablation of duodenal afferents by using RTX or blocking TRPA1 by CHEM-5861528. We found the existence of a neural cross talk between the duodenum and pancreas that can promote acute pancreatitis in response to intraduodenal chemicals. It also proves a previously unexamined mechanism by which alcohol can induce pancreatitis, which is novel both in terms of the site (duodenum), process (neurogenic), and receptor (TRPA1).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transient receptor potential ion channels V4 and A1 contribute to pancreatitis pain in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):G556-71. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00433.2009. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20539005 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic role of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in pancreatic pain and inflammation.Gastroenterology. 2011 Apr;140(4):1283-1291.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.12.033. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21185837 Free PMC article.
-
The preventive effect of resiniferatoxin on the development of cold hypersensitivity induced by spinal nerve ligation: involvement of TRPM8.BMC Neurosci. 2016 Jun 21;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0273-8. BMC Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27329106 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels in pancreatitis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1772(8):869-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2007.02.012. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17428642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+ signalling and pancreatitis: effects of alcohol, bile and coffee.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Feb;27(2):113-20. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2005.12.006. Epub 2006 Jan 6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16406087 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal Models: Challenges and Opportunities to Determine Optimal Experimental Models of Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer.Pancreas. 2019 Jul;48(6):759-779. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001335. Pancreas. 2019. PMID: 31206467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous Allodynia of the Withers in Cattle: An Experimental In Vivo Neuroanatomical Preliminary Investigation of the Dichotomizing Sensory Neurons Projecting into the Reticulum and Skin of the Withers-A Case Study on Two Calves.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jun 6;15(12):1689. doi: 10.3390/ani15121689. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564241 Free PMC article.
-
Intracolonic Mustard Oil Induces Visceral Pain in Mice by TRPA1-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms: Role of Tissue Injury and P2X Receptors.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 21;11:613068. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.613068. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33551815 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Duodenal Microbiota in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis and Healthy Controls.Dig Dis Sci. 2023 Aug;68(8):3341-3353. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-07948-8. Epub 2023 May 31. Dig Dis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37258979 Free PMC article.
-
Energetic etiologies of acute pancreatitis: A report of five cases.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 Nov 15;6(4):243-8. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.243. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26600983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Salam OM, Szolcsanyi J, Mozsik G. Effect of resiniferatoxin on stimulated gastric acid secretory responses in the rat. J Physiol Paris 88: 353–358, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Amir R, Devor M. Functional cross-excitation between afferent A- and C-neurons in dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience 95: 189–195, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Anglade P, Michel C, Roze C. Intrinsic nerves of the pancreas after celiac and superior mesenteric ganglionectomy in rats: a morphologic study of acetylcholinesterase activity and catecholamine histofluorescence. Pancreas 2: 568–577, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Avelino A, Cruz F, Coimbra A. Intravesical resiniferatoxin desensitizes rat bladder sensory fibres without causing intense noxious excitation. A c-fos study. Eur J Pharmacol 378: 17–22, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

