Vitamin D - effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation
- PMID: 23306192
- PMCID: PMC3571641
- DOI: 10.3390/nu5010111
Vitamin D - effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation
Abstract
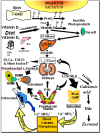
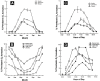
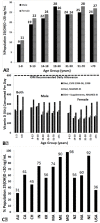
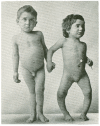
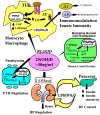
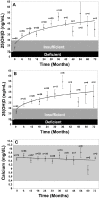
Vitamin D, the sunshine vitamin, has received a lot of attention recently as a result of a meteoric rise in the number of publications showing that vitamin D plays a crucial role in a plethora of physiological functions and associating vitamin D deficiency with many acute and chronic illnesses including disorders of calcium metabolism, autoimmune diseases, some cancers, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and infectious diseases. Vitamin D deficiency is now recognized as a global pandemic. The major cause for vitamin D deficiency is the lack of appreciation that sun exposure has been and continues to be the major source of vitamin D for children and adults of all ages. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of a healthy skeleton throughout life. There remains some controversy regarding what blood level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D should be attained for both bone health and reducing risk for vitamin D deficiency associated acute and chronic diseases and how much vitamin D should be supplemented.
Figures

References
-
- Holick M. Phylogenetic and Evolutionary Aspects of Vitamin D from Phytoplankton to Humans. In: Pang P.K.T., Schreibman M.P., editors. Verebrate Endocrinology: Fundamentals and Biomedical Implications. Academic Press, Inc.; Orlando, FL, USA: 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

