Optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods
- PMID: 23306781
- PMCID: PMC3967601
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-012-9528-0
Optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods
Abstract
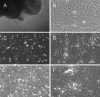
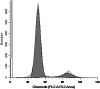
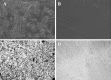
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs) are considered to be an ideal replacement for bone marrow MSCs. However, up to date, there is no convenient and efficient method for hUCMSC isolation and culture. The present study was carried out to explore the modified enzyme digestion for hUCMSC in vitro. Conventional enzyme digestion, modified enzyme digestion, and tissue explant were used on hUCMSCs to compare their efficiencies of isolation and culture, to observe primary cell growth and cell subculture. The results show that the cells cultured using the tissue explant method had a longer culture cycle (P < 0.01) and lower yield of primary cells per centimetre of umbilical cord (P < 0.01) compared with the two enzyme digestion methods. Subculture adherence and cell doubling took significantly less time with the tissue explant method (P < 0.05) than with the conventional enzyme digestion method; however, there was no significant difference between the tissue explant method and the modified enzyme digestion method (P > 0.05). Comparing two enzyme digestion methods, the modified method yielded more cells than did the conventional method (P < 0.01), and primary cell adherence took significantly less time with the modified method than with the conventional method (P < 0.05). Cell cycle analysis of the third-generation hUCMSCs cultured by modified enzyme digestion method indicated that most cells were quiescent. Immunofluorescence staining showed that these cells expressed MSC markers CD44 and CD90. And Von Kossa and oil red O staining detection showed that they could be differentiated into osteoblasts and adipocytes with induction medium in vitro. This study suggests that hUCMSC isolation and culture using 0.2 % collagenase II at 37 °C for digestion of 16-20 h is an effective and simple modified enzyme digestion method.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Primary culture and multiple differentiation potency of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Oct;29(10):1087-93. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24103271 Chinese.
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles exert potent bone protective effects by CLEC11A-mediated regulation of bone metabolism.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 16;10(5):2293-2308. doi: 10.7150/thno.39238. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32089743 Free PMC article.
-
[Biological characteristics of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their differentiation into chondrogenic and osteogenic cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Feb 1;91(5):317-21. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21419006 Chinese.
-
[Comparative study of in vitro hematopoietic supportive capability of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and umbilical cord].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Oct;17(5):1294-300. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19840470 Chinese.
-
Methods of isolation, expansion, differentiating induction and preservation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2012 Dec;125(24):4504-10. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012. PMID: 23253727 Review.
Cited by
-
Double labelling of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with Gd-DTPA and PKH26 and the influence on biological characteristics of hUCMSCs.Int J Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb;96(1):63-72. doi: 10.1111/iep.12111. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Int J Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25649907 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced secretion of hepatocyte growth factor in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 6;13:1070736. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1070736. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36726784 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin beta 3-overexpressing mesenchymal stromal cells display enhanced homing and can reduce atherosclerotic plaque.World J Stem Cells. 2023 Sep 26;15(9):931-946. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.931. World J Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 37900938 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells implantation accelerates cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats via the Wnt signaling pathway.Eur J Med Res. 2019 Feb 8;24(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0366-9. Eur J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30736851 Free PMC article.
-
hUCMSCs Mitigate LPS-Induced Trained Immunity in Ischemic Stroke.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:1746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01746. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conconi MT, Burra P, Di Liddo R, Calore C, Turetta M, Bellini S, Bo P, Nussdorfer GG, Parnigotto PP. CD105 (+) cells from Wharton’s jelly show in vitro and in vivo myogenic differentiative potential. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18:1089–1096. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

