Metallobacteriochlorophylls as potential dual agents for photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy
- PMID: 23306811
- PMCID: PMC3778232
- DOI: 10.1007/s00894-012-1747-y
Metallobacteriochlorophylls as potential dual agents for photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy
Abstract
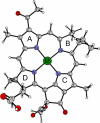
A theoretical analysis of bacteriochlorophyll a containing its non-native divalent metal ions: Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ru, Rh, Pd, and Pt, has been carried out by means of density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The main stress was put on the derivatives with metals, which already found applications as coordination compounds in anti-tumor therapy (Ru, Pt, Pd, and Rh). The idea was to combine their cytotoxic properties with the known suitability of bacteriochlorophylls macrocycle for photodynamic therapy. The geometries of the studied systems are compared and reveal a number of similarities. The cores of the modified bacteriochlorophylls are flat, and the introduced metal ions lie in plane of the macrocycle, showing its large ability to accommodate metal ions of different sizes. However, four metal-nitrogen bonds, linking the central ions with the macrocycle ligand, are not equivalent. Metals are the strongest attached to nitrogens, which come from the pyrrole, which is fused with isocyclic ring. Based on the known spectroscopic data, the absorption properties of the proposed systems are predicted. Finally, it is found that all studied metal-macrocycle adducts are stable in aqueous media. The only exceptions are Mg-BChla (the finding is reflected by experimental facts) and Zn-BChla. The predicted high stability of Ru-, Rh-, Pt- and Pd-bacteriochlorophylls might turn out beneficial for therapeutic purposes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Photophysical properties of heavy atom containing tetrasulfonyl phthalocyanines as possible photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy.J Comput Chem. 2021 Sep 30;42(25):1803-1808. doi: 10.1002/jcc.26714. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Comput Chem. 2021. PMID: 34236090
-
[Synthesis and antitumour activity of metal complexes of bacteriochlorophyll].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2005 Oct;40(10):920-3. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 16408810 Chinese.
-
Metal-based photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy: the future of multimodal oncology?Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2020 Jun;56:23-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 31759225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining Inorganic Chemistry and Biology: The Underestimated Potential of Metal Complexes in Medicine.Chembiochem. 2020 Nov 2;21(21):3044-3046. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000397. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Chembiochem. 2020. PMID: 32896976
-
Lighting up metallohelices: from DNA binders to chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy.Chem Commun (Camb). 2020 Jul 14;56(55):7537-7548. doi: 10.1039/d0cc02194f. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020. PMID: 32573609 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of TD-DFT Theory to Studying Porphyrinoid-Based Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Nov 26;26(23):7176. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237176. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photosensitizers in prostate cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 May 2;8(18):30524-30538. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15496. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28430624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors controlling the reactivity of divalent metal ions towards pheophytin a.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017 Aug;22(6):941-952. doi: 10.1007/s00775-017-1472-1. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 28639057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Institute NC. http://www.cancer.gov.
-
- Bonnett R. Metal complexes for photodynamic therapy. In: McCleverty JA, Meyer TJ, editors. Comprehensive coordination chemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2003.
-
- Rosenbach-Belkin VC L, Fiedor L, Salomon Y, Scherz A. Chlorophyll and bacteriochlorophyll derivatives as photodynamic agents. In: Moser JG, editor. Photodynamic tumor therapy, 2nd and 3rd generation photosensitizers. Amsterdam: Harwood Academic; 1998. pp. 117–125.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources