Warfarin dose prediction in children using pharmacometric bridging--comparison with published pharmacogenetic dosing algorithms
- PMID: 23307232
- PMCID: PMC3651819
- DOI: 10.1007/s00228-012-1466-4
Warfarin dose prediction in children using pharmacometric bridging--comparison with published pharmacogenetic dosing algorithms
Erratum in
- Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;69(9):1737
Abstract
Purpose: Numerous studies have investigated causes of warfarin dose variability in adults, whereas studies in children are limited both in numbers and size. Mechanism-based population modelling provides an opportunity to condense and propagate prior knowledge from one population to another. The main objectives with this study were to evaluate the predictive performance of a theoretically bridged adult warfarin model in children, and to compare accuracy in dose prediction relative to published warfarin algorithms for children.
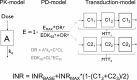
Method: An adult population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model for warfarin, with CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype, age and target international normalized ratio (INR) as dose predictors, was bridged to children using allometric scaling methods. Its predictive properties were evaluated in an external data set of children 0-18 years old, including comparison of dose prediction accuracy with three pharmacogenetics-based algorithms for children.
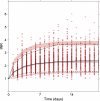
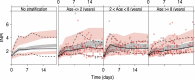
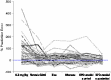
Results: Overall, the bridged model predicted INR response well in 64 warfarin-treated Swedish children (median age 4.3 years), but with a tendency to overpredict INR in children ≤2 years old. The bridged model predicted 20 of 49 children (41 %) within ± 20 % of actual maintenance dose (median age 7.2 years). In comparison, the published dosing algorithms predicted 33-41 % of the children within ±20 % of actual dose. Dose optimization with the bridged model based on up to three individual INR observations increased the proportion within ±20 % of actual dose to 70 %.
Conclusion: A mechanism-based population model developed on adult data provides a promising first step towards more individualized warfarin therapy in children.
Figures
References
-
- Monagle P, Chan AKC, Goldenberg NA, Ichord RN, Journeycake JM, Nowak-Gottl U, Vesely SK. Antithrombotic Therapy in Neonates and Children: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 suppl):e737S–e801S. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

