A study of meiotic segregation in a fertile human population following ovarian stimulation with recombinant FSH-LH
- PMID: 23307445
- PMCID: PMC3585680
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-012-9905-9
A study of meiotic segregation in a fertile human population following ovarian stimulation with recombinant FSH-LH
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the study is to investigate the meiotic segregation in fresh eggs from anonymous egg donors and to analyze the baseline levels of aneuploidy in this population.
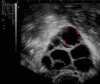
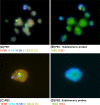
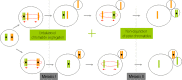
Results: The study includes the largest series of donor eggs so far studied: 203 eggs from donors aged between 20 and 31 years. No diagnosis was obtained in 10.8 % of cases (22/ 203). The biopsy of the first and second polar bodies was completed in a sequential manner on day 0 and day 1 of embryo development. Chromosomes 13, 16, 18, 21 and 22 are analyzed by means of the FISH test. The diagnosable fertilized eggs gave an aneuploidy rate of 19.1 % (31/162), with 83.8 % (26/31) of the errors produced during meiosis I, 12.9 % (4/31) produced during meiosis II, and 3.2 % (1/31) produced during both meiosis I and II. The premature division of sister chromatids is the main source of meiotic error during Meiosis I, resulting in the creation of oocyte aneuploidy.
Conclusions: FISH analysis of the first and second polar body in donor oocytes gave an aneuploidy rate of 19.1 %. This study shows the majority of errors occur during Meiosis I.
Figures
References
-
- Angell RR, Xian J, Keith J. Chromosome anomalies in human oocytes in relation to age. Hum Reprod. 1993;8(7):1047–1054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

