Involvement of PDGF in fibrosis and scleroderma: recent insights from animal models and potential therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 23307576
- PMCID: PMC5570472
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-012-0304-0
Involvement of PDGF in fibrosis and scleroderma: recent insights from animal models and potential therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
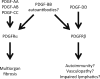
Fibrosis is the principal characteristic of the autoimmune disease known as scleroderma or systemic sclerosis (SSc). Studies published within the last three years suggest central involvement of platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) in SSc-associated fibrosis. PDGFs may also be involved in SSc-associated autoimmunity and vasculopathy. The PDGF signaling pathway is well understood and PDGF receptors are expressed on collagen-secreting fibroblasts and on mesenchymal stem and/or progenitor cells that may affect SSc in profound and unexpected ways. Although much work remains before we fully understand how PDGFs are involved in SSc, there is much interest in using PDGF inhibitors as a therapeutic approach to SSc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

