Anti-inflammatory therapy in chronic disease: challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 23307734
- PMCID: PMC3608517
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1230720
Anti-inflammatory therapy in chronic disease: challenges and opportunities
Abstract
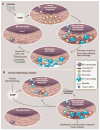
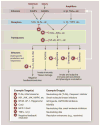
A number of widespread and devastating chronic diseases, including atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease, have a pathophysiologically important inflammatory component. In these diseases, the precise identity of the inflammatory stimulus is often unknown and, if known, is difficult to remove. Thus, there is interest in therapeutically targeting the inflammatory response. Although there has been success with anti-inflammatory therapy in chronic diseases triggered by primary inflammation dysregulation or autoimmunity, there are considerable limitations. In particular, the inflammatory response is critical for survival. As a result, redundancy, compensatory pathways, and necessity narrow the risk:benefit ratio of anti-inflammatory drugs. However, new advances in understanding inflammatory signaling and its links to resolution pathways, together with new drug development, offer promise in this area of translational biomedical research.
Figures

References
-
- Nathan C, Ding A. Cell. 2010;140:871. - PubMed
-
- Castellheim A, Brekke OL, Espevik T, Harboe M, Mollnes TE. Scand J Immunol. 2009;69:479. - PubMed
-
- Kubota T, Koike R. Mod Rheumatol. 2010;20:213. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205. - PubMed
-
- Scrivo R, Vasile M, Bartosiewicz I, Valesini G. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL054591/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HC088093/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057560/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL075662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL087123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL106019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL057560/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL054591/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

