Prioritization of putative metabolite identifications in LC-MS/MS experiments using a computational pipeline
- PMID: 23307777
- PMCID: PMC3719968
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201200306
Prioritization of putative metabolite identifications in LC-MS/MS experiments using a computational pipeline
Abstract
One of the major bottle-necks in current LC-MS-based metabolomic investigations is metabolite identification. An often-used approach is to first look up metabolites from databases through peak mass, followed by verification of the obtained putative identifications using MS/MS data. However, the mass-based search may provide inappropriate putative identifications when the observed peak is from isotopes, fragments, or adducts. In addition, a large fraction of peaks is often left with multiple putative identifications. To differentiate these putative identifications, manual verification of metabolites through comparison between biological samples and authentic compounds is necessary. However, such experiments are laborious, especially when multiple putative identifications are encountered. It is desirable to use computational approaches to obtain more reliable putative identifications and prioritize them before performing experimental verification of the metabolites. In this article, a computational pipeline is proposed to assist metabolite identification with improved metabolome coverage and prioritization capability. Multiple publicly available software tools and databases, along with in-house developed algorithms, are utilized to fully exploit the information acquired from LC-MS/MS experiments. The pipeline is successfully applied to identify metabolites on the basis of LC-MS as well as MS/MS data. Using accurate masses, retention time values, MS/MS spectra, and metabolic pathways/networks, more appropriate putative identifications are retrieved and prioritized to guide subsequent metabolite verification experiments.
© 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
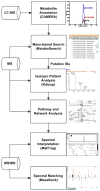

Similar articles
-
LC-MS based serum metabolomics for identification of hepatocellular carcinoma biomarkers in Egyptian cohort.J Proteome Res. 2012 Dec 7;11(12):5914-23. doi: 10.1021/pr300673x. Epub 2012 Nov 1. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 23078175 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolome searcher: a high throughput tool for metabolite identification and metabolic pathway mapping directly from mass spectrometry and using genome restriction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Feb 25;16(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0462-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25887958 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic spectral libraries for data-independent SWATH liquid chromatography mass spectrometry acquisition.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Mar;410(7):1873-1884. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-0860-x. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29411086
-
Challenges and emergent solutions for LC-MS/MS based untargeted metabolomics in diseases.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018 Nov;37(6):772-792. doi: 10.1002/mas.21562. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018. PMID: 29486047 Review.
-
Challenges, progress and promises of metabolite annotation for LC-MS-based metabolomics.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019 Feb;55:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30138778 Review.
Cited by
-
Many InChIs and quite some feat.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2015 Aug;29(8):681-94. doi: 10.1007/s10822-015-9854-3. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2015. PMID: 26081259 No abstract available.
-
Metabolomics and systems pharmacology: why and how to model the human metabolic network for drug discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2014 Feb;19(2):171-82. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.07.014. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Drug Discov Today. 2014. PMID: 23892182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suspect Screening, Prioritization, and Confirmation of Environmental Chemicals in Maternal-Newborn Pairs from San Francisco.Environ Sci Technol. 2021 Apr 20;55(8):5037-5049. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c05984. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Environ Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 33726493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Greef J, Stroobant P, van der Heijden R. The role of analytical sciences in medical systems biology. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2004;8:559–565. - PubMed
-
- Khoo SH, Al-Rubeai M. Metabolomics as a complementary tool in cell culture. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2007;47:71–84. - PubMed
-
- Goodacre R, Vaidyanathan S, Dunn WB, Harrigan GG, Kell DB. Metabolomics by numbers: acquiring and understanding global metabolite data. Trends Biotechnol. 2004;22:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Koek MM, Muilwijk B, van der Werf MJ, Hankemeier T. Microbial metabolomics with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2006;78:1272–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

