The possible role of antioxidant vitamin C in Alzheimer's disease treatment and prevention
- PMID: 23307795
- PMCID: PMC10852723
- DOI: 10.1177/1533317512473193
The possible role of antioxidant vitamin C in Alzheimer's disease treatment and prevention
Abstract
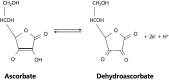
Oxidative stress is suggested to play a major role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Among the antioxidants, vitamin C has been regarded as the most important one in neural tissue. It also decreases β-amyloid generation and acetylcholinesterase activity and prevents endothelial dysfunction by regulating nitric oxide, a newly discovered factor in the pathogenesis and progression of AD. However, clinical trials using antioxidants, including vitamin C, in patients with AD yielded equivocal results. The current article discusses the relevance of vitamin C in the cellular and molecular pathogenesis of AD and explores its therapeutic potential against this neurodegenerative disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and antioxidant neuroprotection].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 1998 Mar;66(3):113-21. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-995246. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 1998. PMID: 9565761 Review. German.
-
Alzheimer's disease and oxidative stress: implications for novel therapeutic approaches.Prog Neurobiol. 1999 Feb;57(3):301-23. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00055-0. Prog Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10096843 Review.
-
Antioxidant approaches for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Expert Rev Neurother. 2010 Jul;10(7):1201-8. doi: 10.1586/ern.10.74. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010. PMID: 20586698 Review.
-
Vitamin C restores behavioral deficits and amyloid-β oligomerization without affecting plaque formation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;26(1):7-18. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101971. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21558647
-
Dietary intakes of vitamin E, vitamin C, and β-carotene and risk of Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;31(2):253-8. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120349. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22543848
Cited by
-
Effect of plasma vitamin C levels on Parkinson's disease and age at onset: a Mendelian randomization study.J Transl Med. 2021 May 24;19(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02892-5. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34030714 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Key Molecules Involved in Spatial Memory Impairment in Triple Transgenic Mice of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;54(5):3843-3858. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9959-2. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27335030
-
Significance of antioxidant potential of plants and its relevance to therapeutic applications.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Jun 11;11(8):982-91. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.12096. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26157352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Compounds in Kimchi Improve the Cognitive and Memory Functions Impaired by Amyloid Beta.Nutrients. 2018 Oct 20;10(10):1554. doi: 10.3390/nu10101554. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30347786 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin C protected human retinal pigmented epithelium from oxidant injury depending on regulating SIRT1.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:750634. doi: 10.1155/2014/750634. Epub 2014 Jul 22. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 25147862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choudhry F, Howlett DR, Richardson JC, Francis PT, Williams RJ. Pro-oxidant diet enhances beta/gamma secretase-mediated APP processing in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(5):960–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

